Task |
|
An atomic unit of work on a project. See activity. |
Task Board |
|
The most basic form of a task board is divided into three columns labeled "To Do," "In Progress," and "Done." Cards are placed in the columns to reflect the current status of that task. |
Task Estimate |
|
An estimate for a particular task. Depending on purpose and formality these estimates are often created and captured as part of ongoing planning and tracking and incorporated in work plans and detailed schedules. |
TCAP |
Transaction Capabilities Application Part |
Transaction Capabilities Application Part, from ITU-T recommendations Q.771-Q.775 or ANSI T1.114 is a protocol for Signalling System 7 networks. Its primary purpose is to facilitate multiple concurrent dialogs between the same sub-systems on the same machines, using Transaction IDs to differentiate these, similar to the way TCP ports facilitate multiplexing connections between the same IP addresses on the Internet. |
Tcl/tk |
|
Tk is a free and open-source, cross-platform widget toolkit that provides a library of basic elements of GUI widgets for building a graphical user interface (GUI) in many programming languages. |
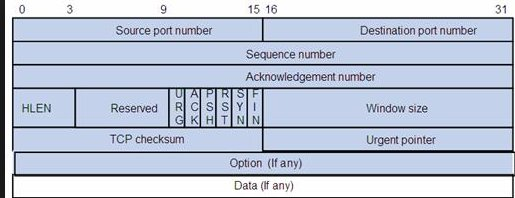
TCP |
Transmission Control Protocol |
The Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) is one of the main protocols of the Internet protocol suite. It originated in the initial network implementation in which it complemented the Internet Protocol (IP). Therefore, the entire suite is commonly referred to as TCP/IP. TCP provides reliable, ordered, and error-checked delivery of a stream of octets (bytes) between applications running on hosts communicating via an IP network. Major internet applications such as the World Wide Web, email, remote administration, and file transfer rely on TCP. Applications that do not require reliable data stream service may use the User Datagram Protocol (UDP), which provides a connectionless datagram service that emphasizes reduced latency over reliability. |
Tcsh |
|
tcsh is a Unix shell based on and compatible with the C shell (csh). It is essentially the C shell with programmable command-line completion, command-line editing, and a few other features. Unlike the other common shells, functions cannot be defined in a tcsh script and the user must use aliases instead (as in csh). It is the native root shell for BSD-based systems such as FreeBSD. |
TDD |
Test Driven Development |
Test-driven development is a style of programming in which three activities are tightly interwoven: coding, testing (in the form of writing unit tests) and design (in the form of refactoring). |
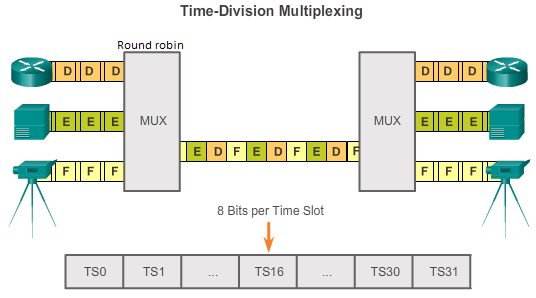
TDM |
Time Division Multiplexing |
Time-division multiplexing (TDM) is a method of transmitting and receiving independent signals over a common signal path by means of synchronized switches at each end of the transmission line so that each signal appears on the line only a fraction of time in an alternating pattern. It is used when the bit rate of the transmission medium exceeds that of the signal to be transmitted. This form of signal multiplexing was developed in telecommunications for telegraphy systems in the late 19th century, but found its most common application in digital telephony in the second half of the 20th century. |
Team |
|
A "team" in the Agile sense is a small group of people, assigned to the same project or effort, nearly all of them on a full-time basis. |
Team Room |
|
The team (ideally the whole team, including the product owner or domain expert) has the use of a dedicated space for the duration of the project, set apart from other groups' activities. |
Technical Debt |
|
Technical debt (also known as design debt or code debt) is a concept in software development that reflects the implied cost of additional rework caused by choosing an easy solution now instead of using a better approach that would take longer. |
Template |
CxTemp |
CxOne template material type. Provides an outline, framework, or container for creating an artifact. See CxOneOverview for description. |
Test |
|
See Testing. May also be used to describe an individual test case. |
Test Activity |
|
A specific test procedure created by combining one or more test techniques and test types. |
Test Case |
TC |
A description of inputs, execution instructions, and expected results, which are created for the purpose of determining whether a specific software feature works correctly or a specific requirement has been satisfied. |
Test Case Specification |
TCS |
Documents the set of test cases needed to verify one or more product features. |
Test Design |
|
Provides a bridge between the test cases and the product's requirements and design. Test design is analogous to software design, and is used when test solutions require a significant amount of analysis and defined structure. |
Test Design Specification |
TDS |
Documents the test design for a group of test cases. |
Test Level |
|
Synonym for test type. |
Test Plan |
TP |
Documents the scope, approach, resources, test items, and schedule of the testing activities. |
Test Technique |
|
Strategy and approach to a test activity. |
Test Type |
|
Standard definitions capturing the what, how, why, and when of a test activity. |
Testing |
|
Software testing CKA. Dynamic execution of software to detect defects. See CxStand_Testing for more information. |
Three Amigos |
|
Three amigos refers to the primary perspectives to examine an increment of work before, during, and after development. Those perspectives are Business, Development, and Testing. |
Three C's |
|
"Card, Conversation, Confirmation" is a formula that captures the components of a User Story. |
Three Questions |
|
The daily meeting is structured around some variant of the following three questions: What have you completed? What will you do next? What is getting in your way? |
TIA |
Telecommunications Industry Association |
The Telecommunications Industry Association (TIA) is accredited by the American National Standards Institute (ANSI) to develop voluntary, consensus-based industry standards for a wide variety of Information and Communication Technologies (ICT) products, and currently represents nearly 400 companies. TIA's Standards and Technology Department operates twelve engineering committees, which develop guidelines for private radio equipment, cellular towers, data terminals, satellites, telephone terminal equipment, accessibility, VoIP devices, structured cabling, data centers, mobile device communications, multimedia multicast, vehicular telematics, healthcare ICT, machine to machine communications, and smart utility networks. |
Timebox |
|
A timebox is a previously agreed period of time during which a person or a team works steadily towards completion of some goal. |
TKIP |
Temporal Key Integrity Protocol |
Temporal Key Integrity Protocol or TKIP /tiːˈkɪp/ is a security protocol used in the IEEE 802.11 wireless networking standard. TKIP was designed by the IEEE 802.11i task group and the Wi-Fi Alliance as an interim solution to replace WEP without requiring the replacement of legacy hardware. This was necessary because the breaking of WEP had left Wi-Fi networks without viable link-layer security, and a solution was required for already deployed hardware. However, TKIP itself is no longer considered secure, and was deprecated in the 2012 revision of the 802.11 standard. |
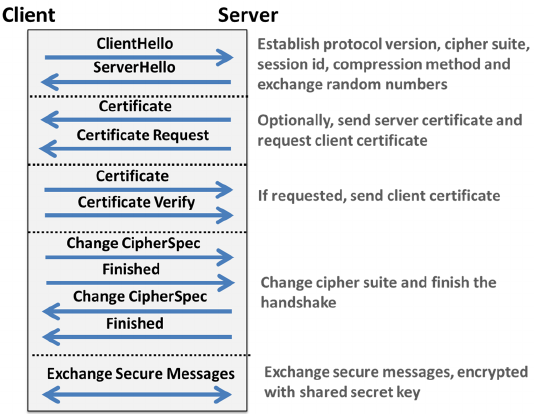
TLS |
Transport Layer Security |
Transport Layer Security (TLS) – and its predecessor, Secure Sockets Layer (SSL), which is now deprecated by the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) – are cryptographic protocols that provide communications security over a computer network. Several versions of the protocols find widespread use in applications such as web browsing, email, instant messaging, and voice over IP (VoIP). Websites are able to use TLS to secure all communications between their servers and web browsers.
|
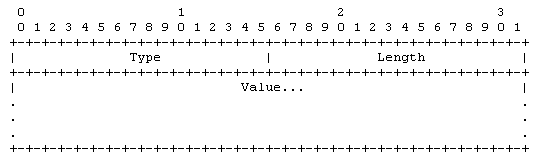
TLV |
Type(Tag), Length and Value |
Within data communication protocols, TLV (type-length-value or tag-length-value) is an encoding scheme used for optional information element in a certain protocol. |
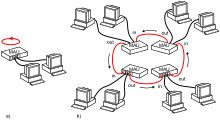
Token Ring |
|
Token Ring local area network (LAN) technology is a communications protocol for local area networks. It uses a special three-byte frame called a "token" that travels around a logical "ring" of workstations or servers. This token passing is a channel access method providing fair access for all stations, and eliminating the collisions of contention-based access methods. |
Top Level Schedule |
|
See Business Schedule. |
Top-Down Estimation |
|
Estimating a system by deriving values for the entire system, and then splitting the total values among decomposed pieces of the system. |
Triple DES |
|
In cryptography, Triple DES (3DES), officially the Triple Data Encryption Algorithm (TDEA or Triple DEA), is a symmetric-key block cipher, which applies the DES cipher algorithm three times to each data block. |
T-Shirt Sizing |
|
T-shirt sizing is a way to practice relative sizing. By comparing stories, you can break them into buckets of extra-small, small, medium, large, and extra-large. |
TTY |
|
A terminal emulator, terminal application, or term, is a program that emulates a video terminal within some other display architecture. Though typically synonymous with a shell or text terminal, the term terminal covers all remote terminals, including graphical interfaces. A terminal emulator inside a graphical user interface is often called a terminal window. |
TUP |
Telephone User Part |
Telephone User Part (TUP) provides conventional PSTN telephony services across the Signalling System No. 7 (SS7) network. TUP was the first layer 4 protocol defined by the standards bodies and as such did not provision for ISDN services. It has now largely been replaced by ISUP. However, it can still be found in operational use in some parts of the world (e.g., China). |
Twisted pair |
|
Twisted pair cabling is a type of wiring in which two conductors of a single circuit are twisted together for the purposes of improving electromagnetic compatibility. Compared to a single conductor or an untwisted balanced pair, a twisted pair reduces electromagnetic radiation, crosstalk between neighboring pairs and improves rejection of external electromagnetic interference |