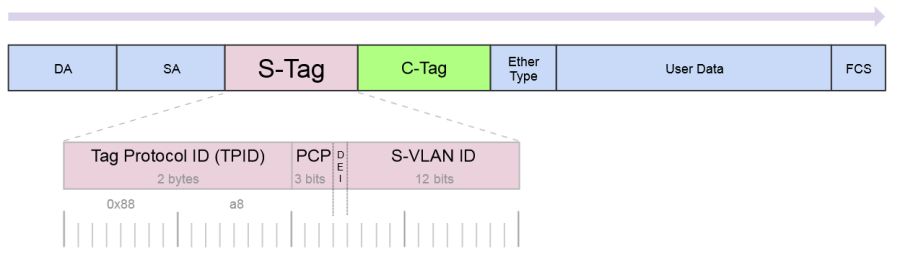
S- Tag | Service VLAN Tag | The IEEE standard 802.1ad provides for double-tagging by service providers so that they can use VLANs allocated internally together with traffic already tagged as VLANs by service provider customers. |
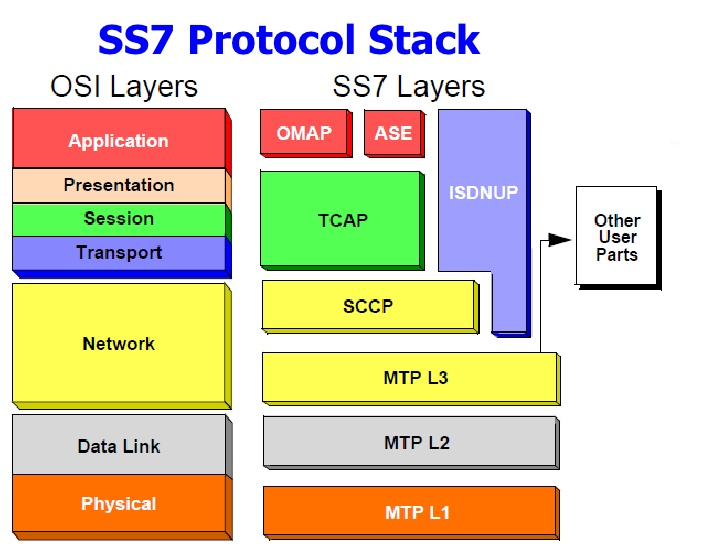
SAAL | Signalling ATM Adaptation Layer | In ATM (Asynchronous Transfer Mode), the SAAL (ATM Adaptation Layer for Signalling) provides reliable transport of signalling messages between peer entities. These signalling messages are carried over a PVC (Permanent Virtual Circuit). |
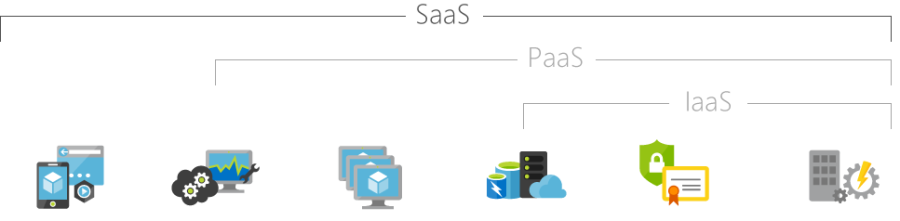
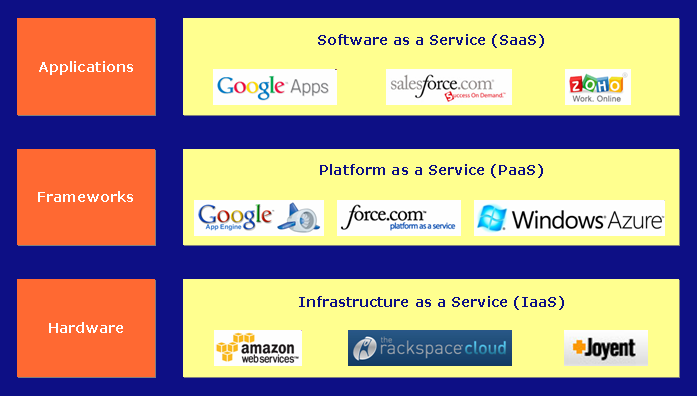
SaaS | Software As A Service | Software as a service is a software licensing and delivery model in which software is licensed on a subscription basis and is centrally hosted. It is sometimes referred to as "on-demand software". SaaS is typically accessed by users using a thin client, e.g. via a web browser. |
SaaS | Software as a Service | Software as a service (SaaS /sæs/) is a software licensing and delivery model in which software is licensed on a subscription basis and is centrally hosted. It is sometimes referred to as "on-demand software", and was formerly referred to as "software plus services" by Microsoft. SaaS is typically accessed by users using a thin client via a web browser. SaaS has become a common delivery model for many business applications, including office software, messaging software, payroll processing software, DBMS software, management software, CAD software, development software, gamification, virtualization, accounting, collaboration, customer relationship management (CRM), Management Information Systems (MIS), enterprise resource planning (ERP), invoicing, human resource management (HRM), talent acquisition, learning management systems, content management (CM), and service desk management. SaaS has been incorporated into the strategy of nearly all leading enterprise software companies |
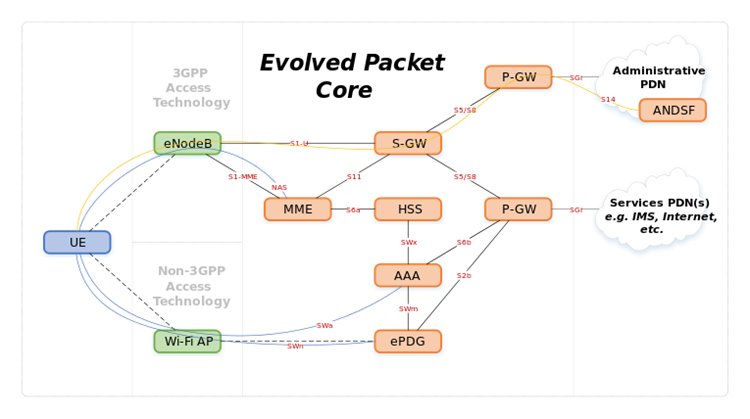
SAE | System Architecture Evolution | System Architecture Evolution (SAE) is the core network architecture of 3GPP's LTE wireless communication standard.
|
SAFe | scaled agile framework enterprise | agile methodology used for software development. |
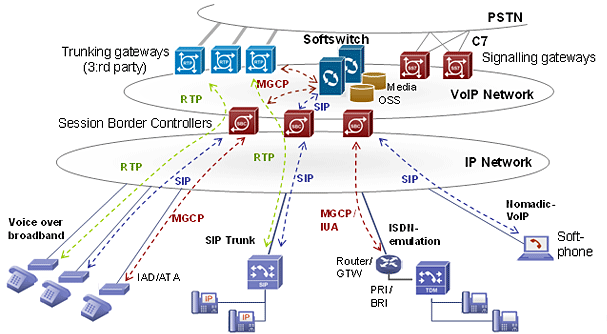
SBC | Session Border Controller | A session border controller (SBC) is a device regularly deployed in Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) networks to exert control over the signalling and usually also the media streams involved in setting up, conducting, and tearing down telephone calls or other interactive media communications. |
Scala | Scala is a general-purpose programming language providing support for functional programming and a strong static type system. Designed to be concise, many of Scala's design decisions aimed to address criticisms of Java. | |
Scaled Agile | agile scaled up to large projects or programmes, for example by having multiple sub-projects, creating tranches of projects, etc. | |
SCCP | Signalling Connection Control Part | The (SCCP) is a network layer protocol that provides extended routing, flow control, segmentation, connection-orientation, and error correction facilities in Signaling System 7 telecommunications networks. SCCP relies on the services of MTP for basic routing and error detection. |
Scenario | A narrative description of an activity or activities which take the form of a story | |
SC-FDMA | Single-carrier FDMA | Single-carrier FDMA (SC-FDMA) is a frequency-division multiple access scheme. It is also called Linearly precoded OFDMA (LP-OFDMA). Like other multiple access schemes (TDMA, FDMA, CDMA, OFDMA), it deals with the assignment of multiple users to a shared communication resource. SC-FDMA can be interpreted as a linearly precoded OFDMA scheme, in the sense that it has an additional DFT processing step preceding the conventional OFDMA processing. |
Schedule | General term for a plan that defines calendar timing, resources, dependencies, and other details for tasks necessary to complete a project or part of a project. CxOne defines two major classes of schedules, business schedules and detailed schedules. | |
Scheduler | In computing, scheduling is the method by which work specified by some means is assigned to resources that complete the work. The work may be virtual computation elements such as threads, processes or data flows, which are in turn scheduled onto hardware resources such as processors, network links or expansion cards. | |
SCM | software configuration management | In software engineering, software configuration management (SCM or S/W CM) is the task of tracking and controlling changes in the software, part of the larger cross-disciplinary field of configuration management.[2] SCM practices include revision control and the establishment of baselines. If something goes wrong, SCM can determine what was changed and who changed it. If a configuration is working well, SCM can determine how to replicate it across many hosts. |
Scratch | Scratch is a visual programming language and online community targeted primarily at children. Using Scratch, users can create online projects and develop them into almost anything by using a simple block-like interface. When they are ready, they then share, and also discuss their creations with each other. Developed by the Lifelong Kindergarten group at the MIT Media Lab, the service is designed to help children (ages 8 and up) learn to utilize their imaginations, practice common sense, and, most importantly, to interact with computers. | |
Scribe | Records issues during an inspection or other formal meeting. | |
Scrum | Scrum is a process framework used to manage product development and other knowledge work. | |
Scrum Master | The scrum master is responsible for ensuring the team lives agile values and principles and follows the practices that the team agreed they would use. | |
Scrum of Scrums | A technique to scale Scrum up to large groups (over a dozen people), consisting of dividing the groups into Agile teams of 5-10. | |
SCTP | Stream Control Transmission Protocol | The (SCTP) is a computer networking communications protocol which operates at the transport layer and serves a role similar to the popular protocols TCP and UDP. It is standardized by IETF in RFC 4960. |
SDES | Session Description protocol Security | SDES (Session Description Protocol Security Descriptions) for Media Streams is a way to negotiate the key for Secure Real-time Transport Protocol. |
SDH | Synchronous Digital Hierarchy | Synchronous optical networking (SONET) and synchronous digital hierarchy (SDH) are standardized protocols that transfer multiple digital bit streams synchronously over optical fiber using lasers or highly coherent light from light-emitting diodes (LEDs). At low transmission rates data can also be transferred via an electrical interface. The method was developed to replace the plesiochronous digital hierarchy (PDH) system for transporting large amounts of telephone calls and data traffic over the same fiber without synchronization problems. |
SDK | Software Development Kit | a set of programs used by a computer programmer to write application programs. |
SDLC | Synchronous Data Link Control | Synchronous Data Link Control (SDLC) is a computer communications protocol. It is the layer 2 protocol for IBM's Systems Network Architecture (SNA). SDLC supports multipoint links as well as error correction. It also runs under the assumption that an SNA header is present after the SDLC header.[1] SDLC was mainly used by IBM mainframe and midrange systems; however, implementations exist on many platforms from many vendors. The use of SDLC (and SNA) is becoming more and more rare, mostly replaced by IP-based protocols or being tunnelled through IP (using AnyNet or other technologies) |
SDLC | systems development life cycle model | one of a number of structured approaches to information system development, created to guide all the processes involved, from an initial feasibility study through maintenance of the completed application. Models include the waterfall model; rapid application development (RAD); joint application development (JAD); the fountain model; the spiral model; build and fix; and synchronize-and-stabilize. |
SDMA | Space-division multiple access | Space-division multiple access (SDMA) is a channel access method based on creating parallel spatial pipes[clarification needed] next to higher capacity pipes through spatial multiplexing and/or diversity, by which it is able to offer superior performance in radio multiple access communication systems.[clarification needed] In traditional mobile cellular network systems, the base station has no information on the position of the mobile units within the cell and radiates the signal in all directions within the cell in order to provide radio coverage. This results in wasting power on transmissions when there are no mobile units to reach, in addition to causing interference for adjacent cells using the same frequency, so called co-channel cells. Likewise, in reception, the antenna receives signals coming from all directions including noise and interference signals. By using smart antenna technology and differing spatial locations of mobile units within the cell, space-division multiple access techniques offer attractive performance enhancements. The radiation pattern of the base station, both in transmission and reception, is adapted to each user to obtain highest gain in the direction of that user. This is often done using phased array techniques. |
SDN | Software Defined Network | Software-defined networking (SDN) technology is an approach to cloud computing that facilitates network management and enables programmatically efficient network configuration in order to improve network performance and monitoring. SDN is meant to address the fact that the static architecture of traditional networks is decentralized and complex while current networks require more flexibility and easy troubleshooting. SDN suggests to centralize network intelligence in one network component by disassociating the forwarding process of network packets (data plane) from the routing process (control plane). The control plane consists of one or more controllers which are considered as the brain of SDN network where the whole intelligence is incorporated. However, the intelligence centralization has its own drawbacks when it comes to security, scalability and elasticity and this is the main issue of SDN |
SDP | Session Description Protocol | The Session Description Protocol (SDP) is a format for describing streaming media communications parameters. The IETF published the original specification as an IETF Proposed Standard in April 1998, and subsequently published a revised specification as an IETF Proposed Standard as RFC 4566 in July 2006. |
SDSL | Symmetrical Digital Subscriber Line | A symmetric digital subscriber line (SDSL) is a digital subscriber line (DSL) that transmits digital data over the copper wires of the telephone network, where the bandwidth in the downstream direction, from the network to the subscriber, is identical to the bandwidth in the upstream direction, from the subscriber to the network. This symmetric bandwidth can be considered to be the opposite of the asymmetric bandwidth offered by asymmetric digital subscriber line (ADSL) technologies, where the upstream bandwidth is lower than the downstream bandwidth. SDSL is generally marketed at business customers, while ADSL is marketed at private as well as business customers.
|
Sed | sed (stream editor) is a Unix utility that parses and transforms text, using a simple, compact programming language. sed was developed from 1973 to 1974 by Lee E. McMahon of Bell Labs, and is available today for most operating systems. sed was based on the scripting features of the interactive editor ed ("editor", 1971) and the earlier qed ("quick editor", 1965–66). sed was one of the earliest tools to support regular expressions, and remains in use for text processing, most notably with the substitution command. Popular alternative tools for plaintext string manipulation and "stream editing" include AWK and Perl. | |
Semaphore | In computer science, a semaphore is a variable or abstract data type used to control access to a common resource by multiple processes in a concurrent system such as a multitasking operating system. Semaphore is simply a variable. This variable is used to solve critical section problems and to achieve process synchronization in the multi processing environment. | |
Sematic Versioning | Given a version number MAJOR.MINOR.PATCH, increment the:
Additional labels for pre-release and build metadata are available as extensions to the MAJOR.MINOR.PATCH format. <valid semver> ::= <version core>
| <version core> "-" <pre-release>
| <version core> "+" <build>
| <version core> "-" <pre-release> "+" <build>
<version core> ::= <major> "." <minor> "." <patch>
<major> ::= <numeric identifier>
<minor> ::= <numeric identifier>
<patch> ::= <numeric identifier>
<pre-release> ::= <dot-separated pre-release identifiers>
<dot-separated pre-release identifiers> ::= <pre-release identifier>
| <pre-release identifier> "." <dot-separated pre-release identifiers>
<build> ::= <dot-separated build identifiers>
<dot-separated build identifiers> ::= <build identifier>
| <build identifier> "." <dot-separated build identifiers>
<pre-release identifier> ::= <alphanumeric identifier>
| <numeric identifier>
<build identifier> ::= <alphanumeric identifier>
| <digits>
<alphanumeric identifier> ::= <non-digit>
| <non-digit> <identifier characters>
| <identifier characters> <non-digit>
| <identifier characters> <non-digit> <identifier characters>
<numeric identifier> ::= "0"
| <positive digit>
| <positive digit> <digits>
<identifier characters> ::= <identifier character>
| <identifier character> <identifier characters>
<identifier character> ::= <digit>
| <non-digit>
<non-digit> ::= <letter>
| "-"
<digits> ::= <digit>
| <digit> <digits>
<digit> ::= "0"
| <positive digit>
<positive digit> ::= "1" | "2" | "3" | "4" | "5" | "6" | "7" | "8" | "9"
<letter> ::= "A" | "B" | "C" | "D" | "E" | "F" | "G" | "H" | "I" | "J"
| "K" | "L" | "M" | "N" | "O" | "P" | "Q" | "R" | "S" | "T"
| "U" | "V" | "W" | "X" | "Y" | "Z" | "a" | "b" | "c" | "d"
| "e" | "f" | "g" | "h" | "i" | "j" | "k" | "l" | "m" | "n"
| "o" | "p" | "q" | "r" | "s" | "t" | "u" | "v" | "w" | "x"
| "y" | "z"
| |
Sequence Model | Specifies the set of object roles and their interactions by showing and describing the messages exchanged. The focus is on the timing of messages. | |
SF | Super Frame | In telecommunications, superframe (SF) is a T1 framing standard. In the 1970s it replaced the original T1/D1 framing scheme of the 1960s in which the framing bit simply alternated between 0 and 1. |
SFTP | Secure File Transfer Protocol | In computing, the SSH File Transfer Protocol (also Secure File Transfer Protocol, or SFTP) is a network protocol that provides file access, file transfer, and file management over any reliable data stream. It was designed by the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) as an extension of the Secure Shell protocol (SSH) version 2.0 to provide secure file transfer capabilities. The IETF Internet Draft states that, even though this protocol is described in the context of the SSH-2 protocol, it could be used in a number of different applications, such as secure file transfer over Transport Layer Security (TLS) and transfer of management information in VPN applications. |
SGML | Standard Generalized Markup Language | The Standard Generalized Markup Language (SGML; ISO 8879:1986) is a standard for defining generalized markup languages for documents. ISO 8879 Annex A.1 defines generalized markup:
<!-- Lunch at the steakhouse -->
<!ELEMENT lunch (meal)+ -- one meal per person -->
<!ELEMENT meal (appetiz?, steak, dessert?,
custname, whopays) +(drink) >
<!-- The plus sign after the content model followed by
one or more elements within parentheses declares an
"inclusion". An inclusion indicates that the elements
can appear anywhere in the element to which they are
attached and in any of its subelements. You can have
one or more DRINK elements any time during MEAL. -->
<!ELEMENT appetiz (soup | salad) >
<!ELEMENT soup EMPTY --soup of the day -->
<!ELEMENT salad EMPTY>
<!ATTLIST salad kind NAME #REQUIRED
dressing (french | 1000isl | bluechse) #REQUIRED>
<!-- The declared value for the attribute DRESSING is
called a "name token group", a series of values separated
by a vertical bar (|). They represent the only possible
values for the attribute. the declared value NAME requires
a value usually comprising up to 8 letters and numbers.
REQUIRED means that one value must be specified for the
attribute. -->
<!ELEMENT steak EMPTY>
<!ATTLIST steak cook (rare|medrare|medium) "medrare"
side (potato|fries|rice) "fries">
<!--The value between quotes is used to force a default
value in case no value is specified for the attribute. -->
<!ELEMENT dessert (cake|applepie)>
<!ELEMENT (cake|applepie) EMPTY>
<!ATTLIST cake kind CDATA #REQUIRED>
<!-- CDATA means any letters, numbers, punctuation,
spaces, or other special characters. This gives you
the possibility of creating long and unique values
for an attribute. This means you can ask for any
cake you want; if the system doesn't recognize the
name, you may not get it. -->
<!ATTLIST applepie hot (hot|warm|cool) #IMPLIED
icecream (yes|no) #IMPLIED
<!-- IMPLIED is an equivalent for optional. The
APPLEPIE comes the way the waiter or waitress prefers
unless you specify otherwise. -->
<!ELEMENT drink (water|beer|cola)>
<!ELEMENT (water|beer|cola) EMPTY>
<!ATTLIST water kind (tap) #FIXED tap>
<!-- The declared value for WATER is fixed by the
system. You can order any kind of fancy water you
want, but all they've got here is tap water. -->
<!ATTLIST beer number NUMBER #REQUIRED>
<!ATTLIST cola type (regular | diet) #CURRENT>
<!-- Beer is ordered by NUMBER from the beer list.
The Default Value CURRENT says that the first time
the element COLA appears, a type must be specified.
That value will be used for the next occurrences
unless you specify another. In other words, you
don't have to re-specify the type of COLA every
time you ask for a refill.-->
<!ELEMENT (custname | whopays) (#PCDATA) >
<!ATTLIST custname account ID #IMPLIED>
<!ATTLIST whopays charge IDREF #REQUIRED>
<!-- The customer's name is not critical data within
the content of the element CUSTNAME: The cashier could
make a typo or use a nickname and the computer would
have difficulty tracking the charge. Instead a unique
identifier is requested - but only if the customer has
an account. However, WHOPAYS has a required IDREF. The
system knows that WHOPAYS may have the same value for
many people's meals (when someone buys for the whole
table) but each CUSTNAME will have a unique ID. The
system will check that the value of the IDREF will be
a legitimate ID. The example below illustrates only
one of several MEALS in the LUNCH. A separate MEAL in
the same LUNCH must include a CUSTNAME with an
ACCOUNTID of "ALEXF" for the CHARGE IDREF to work -->
|
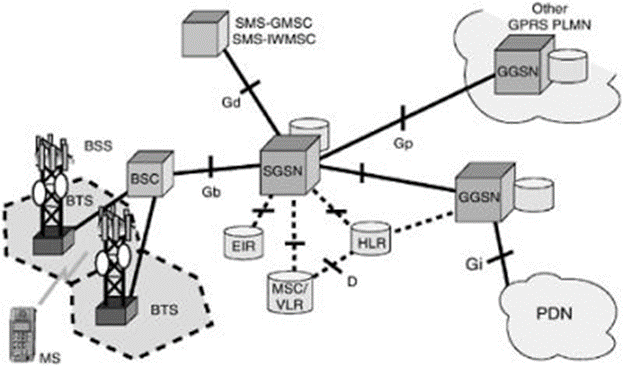
SGSN | Serving GPRS support node | The Serving GPRS Support Node (SGSN) is the node that is serving the MS/UE. The SGSN supports GPRS and/or UMTS. The SGSN keeps track of the location of an individual MS/UE and performs security functions and access control. The SGSN is connected to the GERAN base station system through the Gb or Iu interface and/or to the UTRAN through the Iu interface. A SGSN is responsible for the delivery of data packets from and to the mobile stations within its geographical service area. Its tasks include packet routing and transfer, mobility management (attach/detach and location management), logical link management, and authentication and charging functions. The location register of the SGSN stores location information (e.g., current cell, current VLR) and user profiles (e.g., IMSI, address(es) used in the packet data network) of all GPRS users registered with it.
|
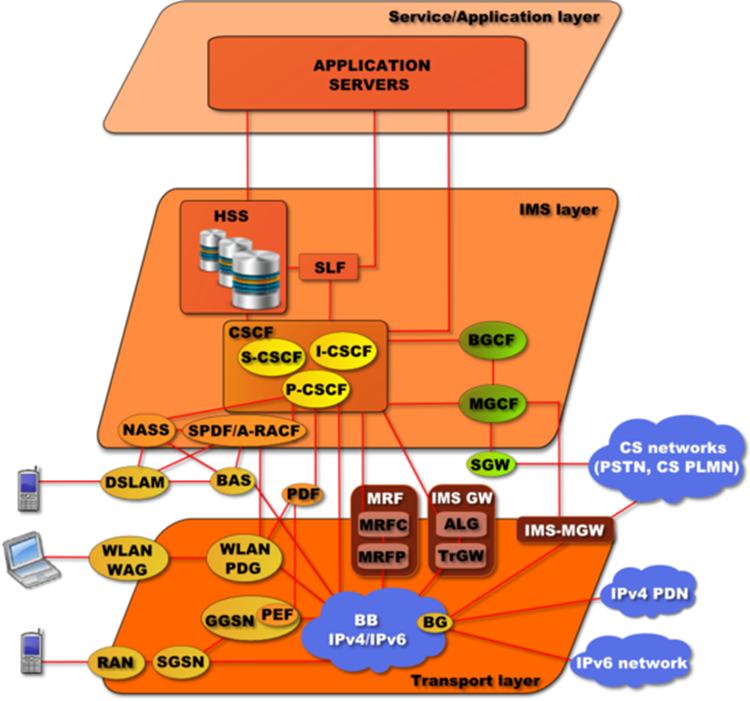
SGW | signalling gateway | A signalling gateway (SGW) interfaces with the signalling plane of the CS. It transforms lower layer protocols as Stream Control Transmission Protocol (SCTP, an IP protocol) into Message Transfer Part (MTP, an Signalling System 7 (SS7) protocol), to pass ISDN User Part (ISUP) from the MGCF to the CS network.
|
S-GW | Serving Gateway | The SGW routes and forwards user data packets, while also acting as the mobility anchor for the user plane during inter-eNodeB handovers and as the anchor for mobility between LTE and other 3GPP technologies (terminating S4 interface and relaying the traffic between 2G/3G systems and PGW). For idle state UEs, the SGW terminates the downlink data path and triggers paging when downlink data arrives for the UE. It manages and stores UE contexts, e.g. parameters of the IP bearer service, network internal routing information. It also performs replication of the user traffic in case of lawful interception.
|
Sh | The Bourne shell (sh) is a shell, or command-line interpreter, for computer operating systems. | |
SHA | Secure Hash Algorithm | The Secure Hash Algorithms are a family of cryptographic hash functions published by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) as a U.S. Federal Information Processing Standard (FIPS), including:
|
Shell Scripting | A shell script is a computer program designed to be run by the Unix shell, a command-line interpreter. The various dialects of shell scripts are considered to be scripting languages. Typical operations performed by shell scripts include file manipulation, program execution, and printing text. A script which sets up the environment, runs the program, and does any necessary cleanup, logging, etc. is called a wrapper. | |
Sidetone | Sidetone is audible feedback to someone speaking when using a handset or headset as an indication of an active transmission. The term is often used in the telecommunication field. | |
Sign Up | for Tasks Members of an Agile development team normally choose which tasks to work on, rather than being assigned work by a manager. (see more | |
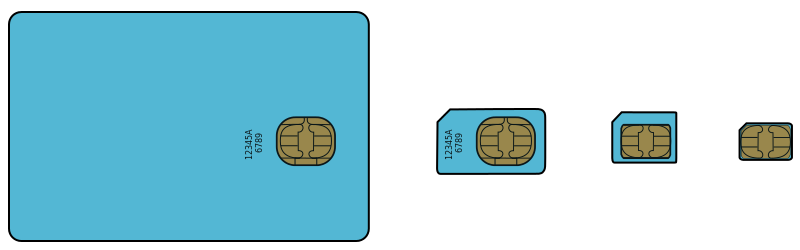
SIM | Subscriber Identity Module | A subscriber identity module or subscriber identification module (SIM), widely known as a SIM card, is an integrated circuit that is intended to securely store the international mobile subscriber identity (IMSI) number and its related key, which are used to identify and authenticate subscribers on mobile telephony devices (such as mobile phones and computers). It is also possible to store contact information on many SIM cards. SIM cards are always used on GSM phones; for CDMA phones, they are only needed for newer LTE-capable handsets. SIM cards can also be used in satellite phones, smart watches, computers, or cameras. |
SIMPLE | Session Initiation Protocol for Instant Messaging and Presence Leveraging Extensions | SIMPLE, the Session Initiation Protocol for Instant Messaging and Presence Leveraging Extensions, is an instant messaging (IM) and presence protocol suite based on Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) managed by the Internet Engineering Task Force. Contrary to the vast majority of IM and presence protocols used by software deployed today, SIMPLE is an open standard like XMPP. |
Simple Design | A team adopting the "simple design" practice bases its software design strategy on a set of "simple design" principles. | |
Simplex | Simplex communication is a communication channel that sends information in one direction only. | |
Single Step Test | Test conducted in a debugging environment by stepping through the source code while executing. | |
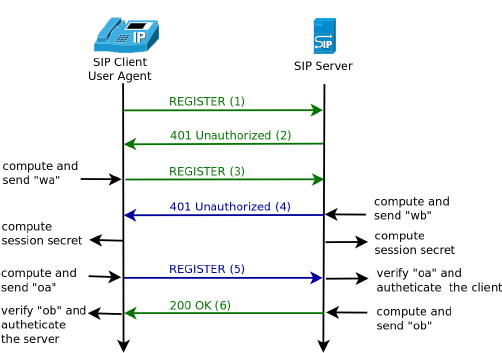
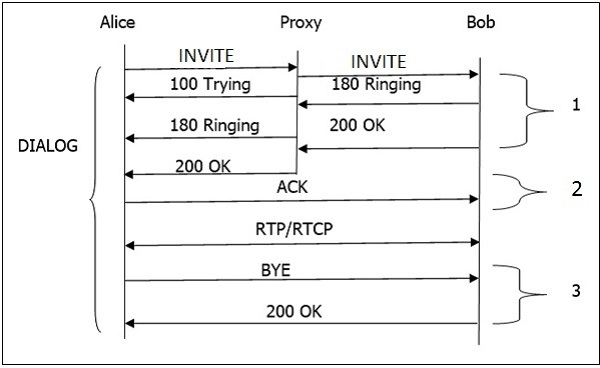
SIP | Session Initiation Protocol | The Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) is a communications protocol for signaling and controlling multimedia communication sessions in applications of Internet telephony for voice and video calls, in private IP telephone systems, as well as in instant messaging over Internet Protocol (IP) networks. |
SIP Trunk | SIP trunking enables the end point's PBX (Phone Exchange System) to send and receive calls via Internet. As SIP is applied for the signalling protocol for multiple real-time application, SIP trunk is able to control voice, video and messaging applications. | |
SISO | single-input and single-output | A single-input and single-output (SISO) system is a simple single variable control system with one input and one output. In radio it is the use of only one antenna both in the transmitter and receiver. |
Skew | Clock skew (sometimes called timing skew) is a phenomenon in synchronous digital circuit systems (such as computer systems) in which the same sourced clock signal arrives at different components at different times i.e. the instantaneous difference between the readings of any two clocks is called their skew. | |
SLA | Service Level Agreement | A service-level agreement (SLA) is a commitment between a service provider and a client. Particular aspects of the service – quality, availability, responsibilities – are agreed between the service provider and the service user. The most common component of SLA is that the services should be provided to the customer as agreed upon in the contract. As an example, Internet service providers and telcos will commonly include service level agreements within the terms of their contracts with customers to define the level(s) of service being sold in plain language terms. In this case the SLA will typically have a technical definition in mean time between failures (MTBF), mean time to repair or mean time to recovery (MTTR); identifying which party is responsible for reporting faults or paying fees; responsibility for various data rates; throughput; jitter; or similar measurable details. |
SLIP | Serial Line Interface Protocol | The Serial Line Internet Protocol (also SLIP) is an encapsulation of the Internet Protocol designed to work over serial ports and modem connections. It is documented in RFC 1055. On personal computers, SLIP has been largely replaced by the Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP), which is better engineered, has more features and does not require its IP address configuration to be set before it is established. On microcontrollers, however, SLIP is still the preferred way of encapsulating IP packets due to its very small overhead. |
SME | Subject Matter Expert | A subject-matter expert (SME) or domain expert is a person who is an authority in a particular area or topic. The term domain expert is frequently used in expert systems software development, and there the term always refers to the domain other than the software domain. A domain expert is a person with special knowledge or skills in a particular area of endeavour (e.g. an accountant is an expert in the domain of accountancy). The development of accounting software requires knowledge in two different domains: accounting and software. Some of the development workers may be experts in one domain and not the other. |
Smoke Test | Test conducted to prove a build. | |
smoke testing | non-exhaustive software testing, ascertaining that the most crucial functions of a prog | |
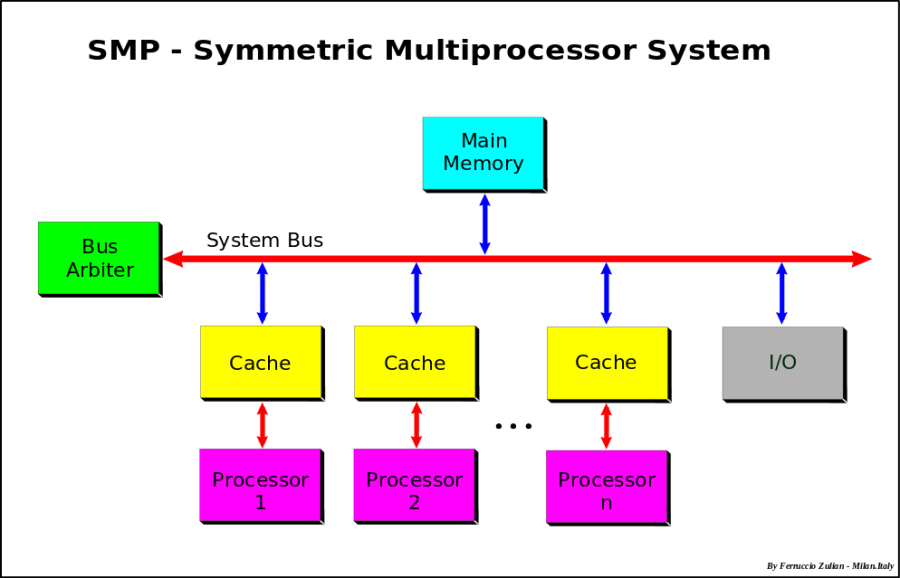
SMP | Symmetric Multiprocessing | Symmetric multiprocessing (SMP) involves a multiprocessor computer hardware and software architecture where two or more identical processors are connected to a single, shared main memory, have full access to all input and output devices, and are controlled by a single operating system instance that treats all processors equally, reserving none for special purposes. Most multiprocessor systems today use an SMP architecture. In the case of multi-core processors, the SMP architecture applies to the cores, treating them as separate processors. |
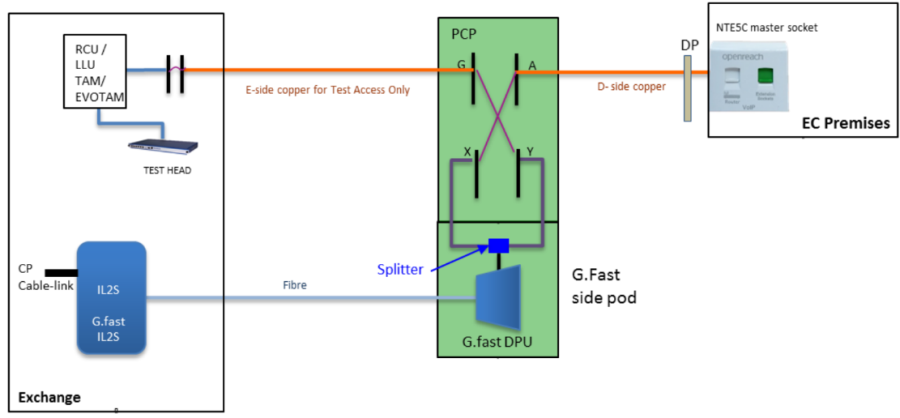
SMPF | Shared Metallic Path Facility | A copper pair to the exchange that goes to two telcos, one for telephone service and one for broadband. Normally this means telephone from BT, and can mean broadband from BT or from another provider. |
SMSC | Short Message service center | A Short Message Service Center (SMSC) is a network element in the mobile telephone network. Its purpose is to store, forward, convert and deliver Short Message Service (SMS) messages.
|
Snake Case | Snake case (or snake_case) is the practice of writing compound words or phrases in which the elements are separated with one underscore character (_) and no spaces, with each element's initial letter usually lowercased within the compound and the first letter either upper- or lowercase—as in "foo_bar" and "Hello_world". It is commonly used in computer code for variable names, and function names, and sometimes computer filenames. | |
SNMP | Simple Network Management Protocol | Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) is an Internet Standard protocol for collecting and organizing information about managed devices on IP networks and for modifying that information to change device behavior. Devices that typically support SNMP include cable modems, routers, switches, servers, workstations, printers, and more. |
SNTP | Simple Network time Protocol | A less complex implementation of NTP, using the same protocol but without requiring the storage of state over extended periods of time, is known as the Simple Network Time Protocol (SNTP). It is used in some embedded devices and in applications where full NTP capability is not required. |
SOA | Service-oriented architecture | Service-oriented architecture (SOA) is a style of software design where services are provided to the other components by application components, through a communication protocol over a network. The basic principles of service-oriented architecture are independent of vendors, products and technologies. A service is a discrete unit of functionality that can be accessed remotely and acted upon and updated independently, such as retrieving a credit card statement online.
|
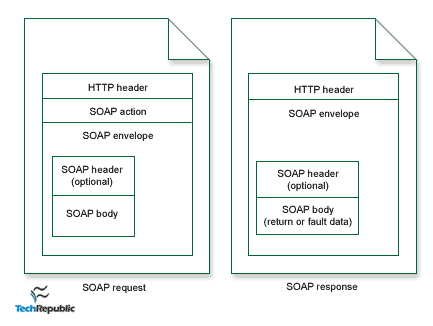
SOAP | Simple Object Access Protocol | SOAP (originally Simple Object Access Protocol) is a messaging protocol specification for exchanging structured information in the implementation of web services in computer networks. Its purpose is to induce extensibility, neutrality and independence. It uses XML Information Set for its message format, and relies on application layer protocols, most often Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) or Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP), for message negotiation and transmission. |
Softswitch | A softswitch (software switch) is a central device in a telecommunications network which connects telephone calls from one phone line to another, across a telecommunication network or the public Internet, entirely by means of software running on a general-purpose computer system. Most landline calls are routed by purpose-built electronic hardware; however, soft switches using general purpose servers and VoIP technology are becoming more popular.[1] | |
Software Change Request | SCR | See change request. |
Software Configuration Management | SCM | See configuration management. |
Software Development Plan | SDP | Sometimes used as a synonym for project plan on software focused projects. |
Software Engineering Body of Knowledge | SWEBOK | IEEE led industry effort to define a body of knowledge for software engineering. Is intended to support defining software engineering as a profession. CxOne bases its top-level organization on SWEBOK. |
Software Engineering Lab | SEL | NASA lab developed to improving the software process used to develop systems at Goddard. |
Software Engineering Process Group | SEPG | Provides experienced and objective technical oversight from individuals who are not directly involved in the project. Also provides process improvement input for projects and the organization. |
Software Requirements Specification | SRS | A text based document that captures the requirements for a software system. Often used in conjunction with other requirements techniques such as modeling and prototyping to provide a complete view of system requirements. |
SoGEA | Single Order Generic Ethernet Access | • Single order Generic Ethernet Access. |
SONET | Synchronous Optical Network | Synchronous optical networking (SONET) and synchronous digital hierarchy (SDH) are standardized protocols that transfer multiple digital bit streams synchronously over optical fiber using lasers or highly coherent light from light-emitting diodes (LEDs). At low transmission rates data can also be transferred via an electrical interface. The method was developed to replace the plesiochronous digital hierarchy (PDH) system for transporting large amounts of telephone calls and data traffic over the same fiber without synchronization problems. |
Source Code | In computing, source code is any collection of code, possibly with comments, written using a human-readable programming language, usually as plain text. The source code of a program is specially designed to facilitate the work of computer programmers, who specify the actions to be performed by a computer mostly by writing source code. The source code is often transformed by an assembler or compiler into binary machine code understood by the computer. The machine code might then be stored for execution at a later time. Alternatively, source code may be interpreted and thus immediately executed. | |
SPEEX | Speex is an audio compression format specifically tuned for the reproduction of human speech and also a free software speech codec that may be used on VoIP applications and podcasts. It is based on the CELP speech coding algorithm. Speex claims to be free of any patent restrictions and is licensed under the revised (3-clause) BSD license. It may be used with the Ogg container format or directly transmitted over UDP/RTP. It may also be used with the FLV container format. | |
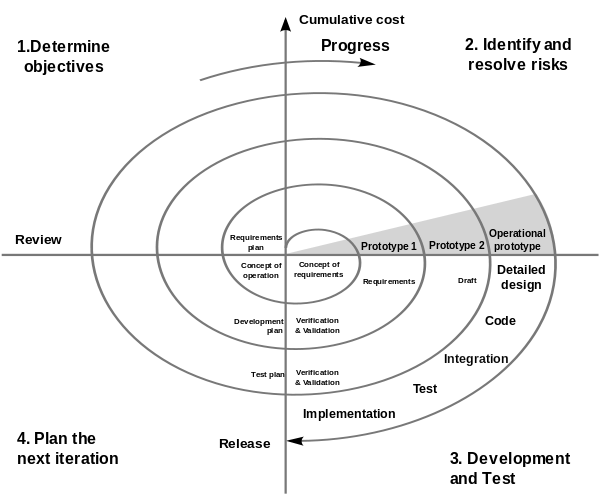
Spiral Lifecycle | A set of mini-projects cumulating in final delivery. Each mini-project focuses on addressing the current major project risk(s). | |
Sponsor | Synonym for project sponsor. | |
Sprial Model | The spiral model is a risk-driven process model generator for software projects. Based on the unique risk patterns of a given project, the spiral model guides a team to adopt elements of one or more process models, such as incremental, waterfall, or evolutionary prototyping. | |
Sprint Planning | Sprint planning is an event that occurs at the beginning of a sprint where the team determines the product backlog items they will work on during that sprint. | |
Sprint retrospective | a review of a Sprint providing lessons learned with the aim of promoting continuous improvement. | |
Sprints | a short development phase within a larger project defined by available time ('timeboxes') and resources. | |
SQL | SQL is a domain-specific language used in programming and designed for managing data held in a relational database management system (RDBMS), or for stream processing in a relational data stream management system (RDSMS). It is particularly useful in handling structured data where there are relations between different entities/variables of the data. SQL offers two main advantages over older read/write APIs like ISAM or VSAM: first, it introduced the concept of accessing many records with one single command; and second, it eliminates the need to specify how to reach a record, e.g. with or without an index. | |
SS7 | Signaling System 7 | Signaling System No. 7 (SS7) is a set of telephony signaling protocols developed in 1975, which is used to set up and tear down most of the world's public switched telephone network (PSTN) telephone calls. It also performs number translation, local number portability, prepaid billing, Short Message Service (SMS), and other mass market services. |
SSADM | Structured Systems Analysis & Design Method | a widely-used computer application development method in the UK that divides an application development project into modules, stages, steps, and tasks, and provides a framework for describing projects in a fashion suited to managing the project. |
SSH | Secure Shell | Secure Shell (SSH) is a cryptographic network protocol for operating network services securely over an unsecured network. The best known example application is for remote login to computer systems by users. |
SSID | Service Set Identifier | Logical wireless networks (including extended service sets) are identified by SSIDs, which serve as "network names" and are typically natural language labels. |
SSIS | SQL Server Integration Services | SQL Server Integration Services (SSIS) is a component of the Microsoft SQL Server database software that can be used to perform a broad range of data migration tasks. |
SSL | Secure Sockets Layer | See TLS |
Stack | The protocol stack or network stack is an implementation of a computer networking protocol suite or protocol family. The terms are often used interchangeably; strictly speaking, the suite is the definition of the Communications protocols, and the stack is the software implementation of them. | |
Staff Days | A measure of effort indicating how much work needs to take place on an activity or artifact. Is often used to differentiate from calendar days. Also applies to other units of time. | |
Stage | Often used as a synonym for phase. May be more precisely used to define groupings of milestones, in terms of a hierarchy with phases that are made up of stages. | |
Staged Delivery Lifecycle | Project development occurs in stages, where the most critical functionality is delivered first | |
Stakeholder | Individuals or entities with significant investment in the outcome of a project. Normally includes clients, customers, internal/external organizations affected by the project, etc. | |
Standard | CxStand | CxOne standard material type. Defined terminology, processes, policies, knowledge, and/or guidelines. See CxOneOverview for description. |
Statistical Estimation | Estimation techniques that utilize historical data coupled with a statistically derived model to provide output estimates based on input characteristics. Most often use size as an input to predict effort and time. Works best when calibrated with relevant historical data and influence modifiers. | |
STB | Set Top Box | A set-top box (STB) or set-top unit (STU) (one type also colloquially known as a cable box) is an information appliance device that generally contains a TV-tuner input and displays output to a television set and an external source of signal, turning the source signal into content in a form that then be displayed on the television screen or other display device. They are used in cable television, satellite television, and over-the-air television systems, as well as other uses. |
Story Mapping | Story mapping consists of ordering user stories along two independent dimensions. | |
Story Splitting | Splitting consists of breaking up one user story into smaller ones, while preserving the property that each user story separately has measurable business value. | |
Storyboard | A sequence of images which depict a scenario or use case. | |
STP | Spanning Tree Protocol | The Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) is a network protocol that builds a loop-free logical topology for Ethernet networks. The basic function of STP is to prevent bridge loops and the broadcast radiation that results from them. Spanning tree also allows a network design to include backup links to provide fault tolerance if an active link fails. |
Strategy | The way a problem or issue is approached. | |
STUN | Session Traversal Utilities for NAT | (STUN) is a standardized set of methods, including a network protocol, for traversal of network address translator (NAT) gateways in applications of real-time voice, video, messaging, and other interactive communications. |
Subversion | Apache Subversion (often abbreviated SVN, after its command name svn) is a software versioning and revision control system distributed as open source under the Apache License. Software developers use Subversion to maintain current and historical versions of files such as source code, web pages, and documentation. Its goal is to be a mostly compatible successor to the widely used Concurrent Versions System (CVS). | |
Sustainable Pace | The team aims for a work pace that they would be able to sustain indefinitely. | |
SVC | Soft Virtual Service | Switched virtual circuits (SVCs) are generally set up on a per-call basis and are disconnected when the call is terminated; however, a permanent virtual circuit (PVC) can be established as an option to provide a dedicated circuit link between two facilities. PVC configuration is usually preconfigured by the service provider. Unlike SVCs, PVC are usually very seldom broken/disconnected. |
Swift | Swift is a general-purpose, multi-paradigm, compiled programming language developed by Apple Inc. for iOS, macOS, watchOS, tvOS, and Linux. Swift is designed to work with Apple's Cocoa and Cocoa Touch frameworks and the large body of existing Objective-C (ObjC) code written for Apple products. It is built with the open source LLVM compiler framework and has been included in Xcode since version 6. On platforms other than Linux, it uses the Objective-C runtime library which allows C, Objective-C, C++ and Swift code to run within one program | |
Switch | A network switch (also called switching hub, bridging hub, officially MAC bridge) is a computer networking device that connects devices together on a computer network by using packet switching to receive, process, and forward data to the destination device. | |
System | A functional entity, normally composed of software, hardware, and closely related operational processes. | |
System Test | Test focused on verifying operational behavior of the entire system, using a project build and the system test environment. | |
System Test Environment | Environment that simulates operational environment and conditions as closely as possible. | |
SystemX | 2nd national digital telephone exchange system to be used in the United Kingdom. | System X was developed by the UK Post Office (later to become British Telecom), GEC, Plessey (later to be Marconi), and Standard Telephones and Cables (STC). |