R |
|
R is a programming language and free software environment for statistical computing and graphics that is supported by the R Foundation for Statistical Computing. The R language is widely used among statisticians and data miners for developing statistical software and data analysis. Polls, surveys of data miners, and studies of scholarly literature databases show that R's popularity has increased substantially in recent years. As of June 2018, R ranks 10th in the TIOBE index, a measure of popularity of programming languages. |
||
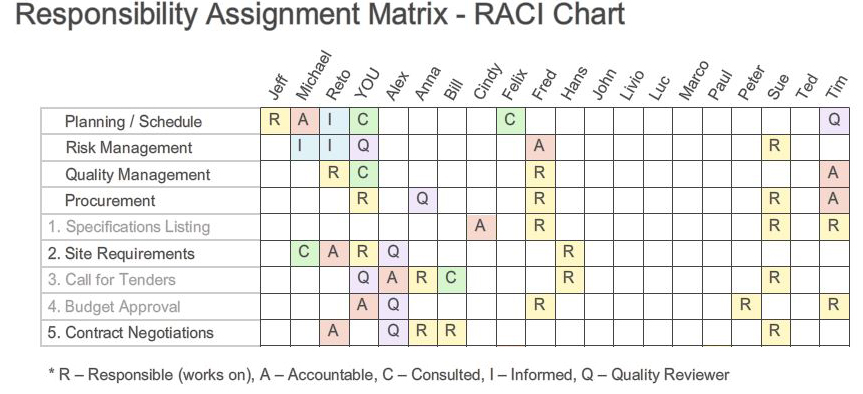
RACI |
Responsible, Accountable, Consulted, and Informed |
A responsibility assignment matrix (RAM), also known as RACI matrix or linear responsibility chart (LRC), describes the participation by various roles in completing tasks or deliverables for a project or business process. It is especially useful in clarifying roles and responsibilities in cross-functional/departmental projects and processes. |
||
RAD |
rapid application development |
an approach based on the concept that products can be developed faster and of higher quality through: gathering requirements using workshops or focus groups; prototyping and early, reiterative user testing of designs; reusing software components; and using less formality in communication documents, such as reviews. |
||
RAD |
rapid application development |
agile development method; enables developers to build solutions quickly by talking directly to end users to meet business requirement. |
||
RAD Environment |
|
Refers to a software tool the combines one or more programming languages with an IDE and a toolbox of modular software user interface components. |
||
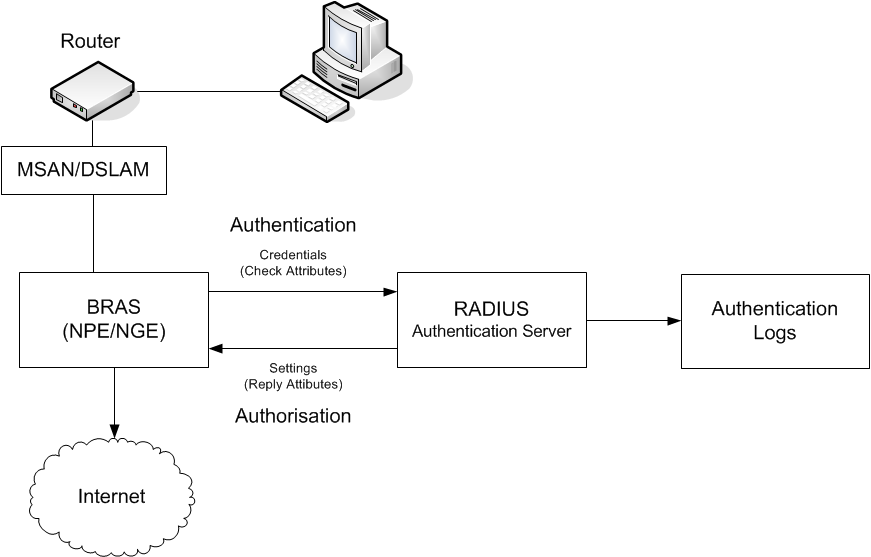
Radius |
Remote Authentication Dial In User Service |
|
||
Rainbow |
|
Opal business solutions, gata does into Remedy 7.6 (Service inventory) |
||
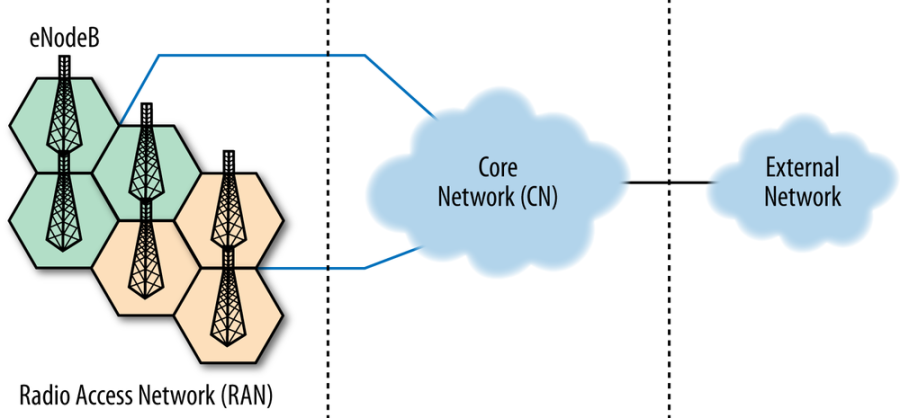
RAN |
radio access network |
A radio access network (RAN) is part of a mobile telecommunication system. It implements a radio access technology. Conceptually, it resides between a device such as a mobile phone, a computer, or any remotely controlled machine and provides connection with its core network (CN). Depending on the standard, mobile phones and other wireless connected devices are varyingly known as user equipment (UE), terminal equipment, mobile station (MS), etc. RAN functionality is typically provided by a silicon chip residing in both the core network as well as the user equipment.
|
||
RANAP |
Radio Access Network Application Part |
In telecommunications networks, RANAP (an acronym for Radio Access Network Application Part) is a protocol specified by 3GPP in TS 25.413 and used in UMTS for signaling between the Core Network, which can be a MSC or SGSN, and the UTRAN. RANAP is carried over Iu-interface. |
||
RANCID |
Really Awesome New Cisco config Differ |
A network management application released under a BSD-style license. RANCID uses Expect to connect to the routers, send some commands and put the results in files. |
||
Rapid Application Development |
RAD |
A collection of software development techniques that focuses on user interface prototyping techniques and tools to create applications in an incremental fashion. |
||
RARP |
Dynamic IP Address Allocation – Reverse Address Resolution protocol |
The Reverse Address Resolution Protocol (RARP) is an obsolete computer networking protocol used by a client computer to request its Internet Protocol (IPv4) address from a computer network, when all it has available is its link layer or hardware address, such as a MAC address. The client broadcasts the request and does not need prior knowledge of the network topology or the identities of servers capable of fulfilling its request. |
||
RAS |
Remote Access Server |
Refers to any combination of hardware and software that enable the remote access to a network; often used in dial-up networking scenarios. These devices typically use a RADIUS service. |
||
RAS |
Registration, Admission, and Status |
Registration, admission, and status (RAS) is a component of a network protocol that involves the addition of (or refusal to add) new authorized users, the admission of (or refusal to admit) authorized users based on available bandwidth, and the tracking of the status of all users. Formally, RAS is part of the H.225 protocol for H.323 communications networks, designed to support multimedia bandwidths. RAS is an important signalling component in networks using voice over IP (VoIP). |
||
RDBMS |
relational database management system |
A relational database management system (RDBMS) is a database management system (DBMS) based on the relational model invented by Edgar F. Codd at IBM's San Jose Research Laboratory. Most databases in widespread use today are based on his relational database model. |
||
RDP |
Remote Desktop Protocol |
Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) is a proprietary protocol developed by Microsoft, which provides a user with a graphical interface to connect to another computer over a network connection. The user employs RDP client software for this purpose, while the other computer must run RDP server software. |
||
Reading Inspection |
|
An inspection in which all components of the full inspection process are done except the inspection meeting. |
||
refactoring |
|
a process that improves the internal structure of a software system without changing its external behaviour. |
||
Refactoring |
|
Refactoring consists of improving the internal structure of an existing program's source code, while preserving its external behavior. |
||
Reference |
CxRef |
CxOne reference material type, see CxOneOverview for description. |
||
regression testing |
|
the process of testing changes to computer programs to make sure that the older programming still works with the new changes. |
||
Regular expression |
|
A regular expression, regex or regexp (sometimes called a rational expression) is, in theoretical computer science and formal language theory, a sequence of characters that define a search pattern. Usually this pattern is then used by string searching algorithms for "find" or "find and replace" operations on strings, or for input validation. |
||
Relative Estimation |
|
Relative estimation consists of estimating tasks or user stories by comparison or by grouping of items of equivalent difficulty. |
||
Release |
|
A software release. Providing a deployable version of a software system to a customer, e.g., test group, client, customer, etc. |
||
Release Management |
|
The identification, packaging, and delivery of the elements of the product to an external or internal customer. |
||
Release Test |
|
Test to ensure software is ready for a release. |
||
Requirement |
|
A detailed description of what the software is supposed to do |
||
Requirements |
|
are written as 'stories' that are collated into a prioritised list called the 'Backlog'. |
||
Requirements |
|
Software requirements. Determining and capturing what a software system should do. Also denotes the requirements CKA. See CxStand_Requirements for more information. |
||
Requirements Lead |
|
Responsible for defining, maintaining, and tracing product requirements. Ensures proper end-user documentation is developed from the requirements. |
||
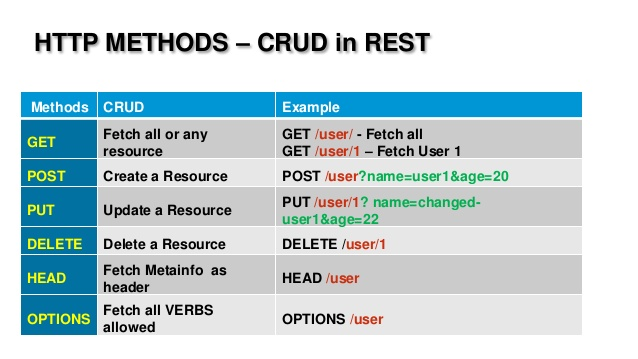
REST |
Representational State Transfer |
Representational State Transfer (REST) is an architectural style that defines a set of constraints and properties based on HTTP. Web Services that conform to the REST architectural style, or RESTful web services, provide interoperability between computer systems on the Internet. REST-compliant web services allow the requesting systems to access and manipulate textual representations of web resources by using a uniform and predefined set of stateless operations. Other kinds of web services, such as SOAP web services, expose their own arbitrary sets of operations. |
||
Review |
|
A defined process in which people who are not the author of an artifact look over it with the intent of finding issues. Reviews range in formality from desk checks to inspections. |
||
Reviewer |
|
A person who participates in a review to identify issues in an artifact |
||
Revision |
|
An instance of a specific artifact, generally as noted by an automated system. |
||
Revision Control |
RC |
The identification, storage, and management of projects artifacts and the revisions over time of those artifacts. Usually performed to artifacts stored in electronic form, through an automated system. |
||
Rework |
|
Any unforeseen or unplanned activity necessary to bring an artifact into conformance with project needs. Compare to update. |
||
RFC |
RF connector |
A coaxial RF connector (radio frequency connector) is an electrical connector designed to work at radio frequencies in the multi-megahertz range. RF connectors are typically used with coaxial cables and are designed to maintain the shielding that the coaxial design offers. Better models also minimize the change in transmission line impedance at the connection in order to reduce signal reflection and power loss. As the frequency increases, transmission line effects become more important, with small impedance variations from connectors causing the signal to reflect rather than pass through. An RF connector must not allow external signals into the circuit through electromagnetic interference and capacitive pickup. |
||
RFC |
Request For Comment |
A Request for Comments (RFC) is a formal document drafted by the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) that describes the specifications for a particular technology. When an RFC is ratified, it becomes a formal standards document. |
||
RIP |
Routing Information Protocol |
The Routing Information Protocol (RIP) is one of the oldest distance-vector routing protocols which employ the hop count as a routing metric. RIP prevents routing loops by implementing a limit on the number of hops allowed in a path from source to destination. The largest number of hops allowed for RIP is 15, which limits the size of networks that RIP can support. |
||
Risk |
|
An undesirable outcome. |
||
Risk Analysis |
|
Assesses risks for the likelihood and impact of occurrence. |
||
Risk Identification |
|
The elicitation and determination of current risks. |
||
Risk List |
|
A technique for extrinsic risk management that documents current and previous risks. Normally includes analysis information and mitigation plans. |
||
Risk Management |
|
A process or activity involving formal or informal means of identification, control, and elimination of project risk. Risk management may be explicit, or may be implicit in other activities (see intrinsic and extrinsic risk management). Managing identified risks is part of corrective activity management. |
||
Risk Mitigation |
|
The planning or steps taken to minimize either the probability or impact of a risk. |
||
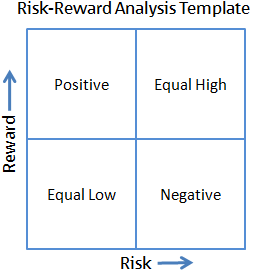
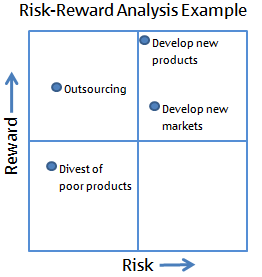
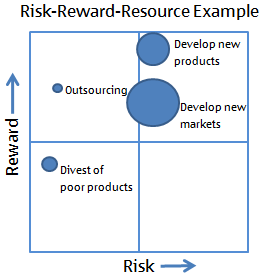
Risk Reward Matric |
|
A risk-reward analysis is a very simple tool which can help you assess the risk and reward profile of completely different options. It works in the same way as a risk-return analysis which you may already be familiar with.
|
||
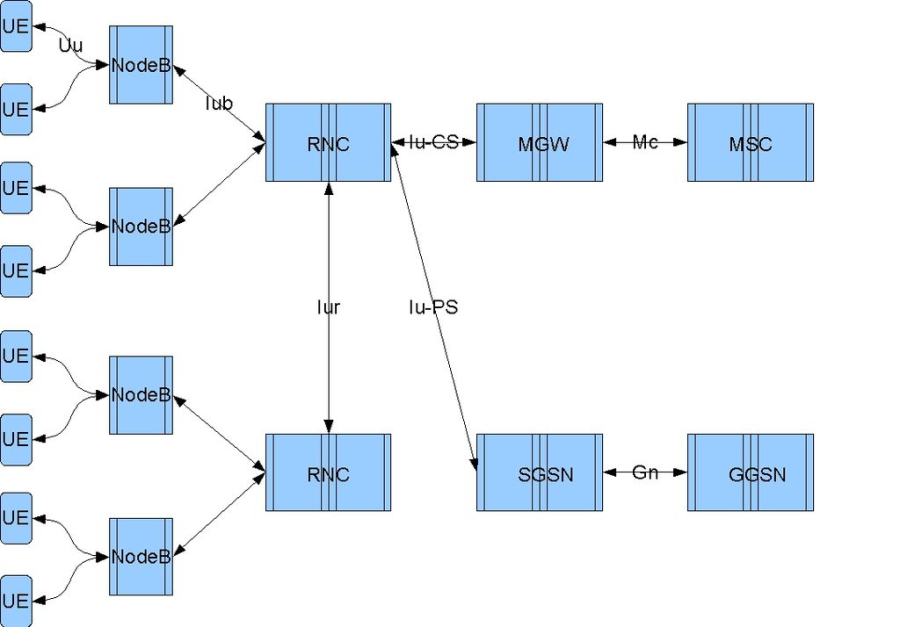
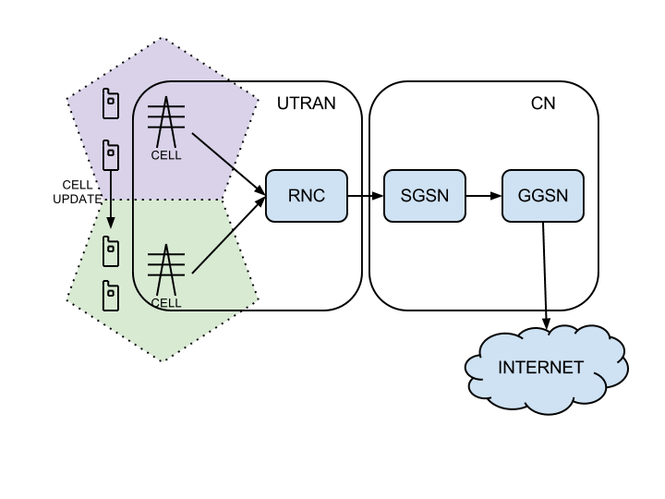
RNC |
Radio Network Controller |
The Radio Network Controller (or RNC) is a governing element in the UMTS radio access network (UTRAN) and is responsible for controlling the Node Bs that are connected to it. The RNC carries out radio resource management, some of the mobility management functions and is the point where encryption is done before user data is sent to and from the mobile. The RNC connects to the Circuit Switched Core Network through Media Gateway (MGW) and to the SGSN (Serving GPRS Support Node) in the Packet Switched Core Network.
|
||
RNSAP |
Radio Network Subsystem Application Part |
RNSAP (Radio Network Subsystem Application Part) is a 3GPP signalling protocol responsible for communications between RNCs Radio Network Controllers defined in 3GPP specification TS 25.423.[1] It is carried on the lur interface and provides functionality needed for soft handovers and SRNS (Serving Radio Network Subsystem) relocation (handoff between RNCs).It defines signalling between RNCs, including SRNC(Serving RNC) and DRNC(drift RNC). |
DRNC |
|
IUR |
|
RNSAP |
||
|
|
|
Converge protol |
|
|
|
|
AAL5 |
ATM |
Role-feature-reason |
|
The "role-feature-reason" template is one of the most commonly recommended aids to write user stories: As a ... I want ... So that ... |
||
Rolling Wave Planning |
|
Planning a project, often with an iterative lifecycle, with a sliding window of visibility. Items closer to the present are planned and tracked with greater detail than items further in the future. See project headlights. |
||
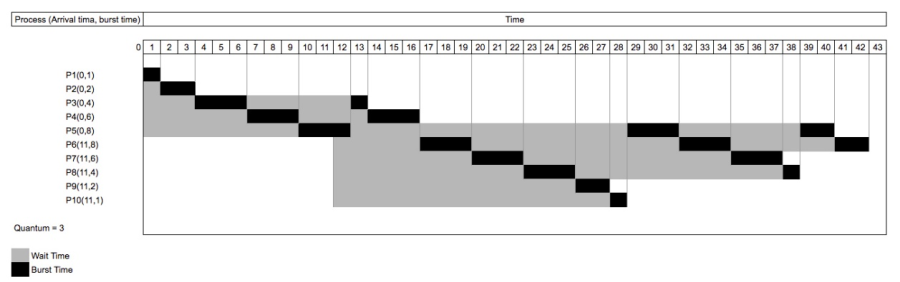
Round Robin |
|
Round-robin (RR) is one of the algorithms employed by process and network schedulers in computing. As the term is generally used, time slices (also known as time quanta) are assigned to each process in equal portions and in circular order, handling all processes without priority (also known as cyclic executive). Round-robin scheduling is simple, easy to implement, and starvation-free. Round-robin scheduling can also be applied to other scheduling problems, such as data packet scheduling in computer networks. It is an operating system concept. |
||
Router |
|
A router is a networking device that forwards data packets between computer networks. Routers perform the traffic directing functions on the Internet. Data sent through the internet, such as a web page or email, is in the form of data packets. A packet is typically forwarded from one router to another router through the networks that constitute an internetwork until it reaches its destination node. |
||
RPC |
|
In distributed computing, a remote procedure call (RPC) is when a computer program causes a procedure (subroutine) to execute in a different address space (commonly on another computer on a shared network), which is coded as if it were a normal (local) procedure call, without the programmer explicitly coding the details for the remote interaction. That is, the programmer writes essentially the same code whether the subroutine is local to the executing program, or remote. This is a form of client–server interaction (caller is client, executor is server), typically implemented via a request–response message-passing system. In the object-oriented programming paradigm, RPC calls are represented by remote method invocation (RMI). The RPC model implies a level of location transparency, namely that calling procedures is largely the same whether it is local or remote, but usually they are not identical, so local calls can be distinguished from remote calls. Remote calls are usually orders of magnitude slower and less reliable than local calls, so distinguishing them is important. |
||
RRC |
Radio Resource Control |
The Radio Resource Control (RRC) protocol is used in UMTS and LTE on the Air interface. It is a layer that exists between UE and eNB and exists at the IP level. This protocol is specified by 3GPP in TS 25.331 for UMTS and in TS 36.331 for LTE. RRC messages are transported via the PDCP-Protocol. |
||
RSTP |
Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol |
In 2001, the IEEE introduced Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP) as 802.1w. RSTP provides significantly faster spanning tree convergence after a topology change, introducing new convergence behaviors and bridge port roles to do this. RSTP was designed to be backwards-compatible with standard STP. |
||
RSVP |
Resource Reservation Protocol |
The Resource Reservation Protocol (RSVP) is a transport layer protocol designed to reserve resources across a network for quality of service (QoS) using the integrated services model. RSVP operates over an IPv4 or IPv6 and provides receiver-initiated setup of resource reservations for multicast or unicast data flows. It does not transport application data but is similar to a control protocol, like Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) or Internet Group Management Protocol (IGMP). RSVP is described in RFC 2205. |
||
RTCP |
Real-Time Control Protocol |
The RTP Control Protocol (RTCP) is a sister protocol of the Real-time Transport Protocol (RTP). Its basic functionality and packet structure is defined in RFC 3550. RTCP provides out-of-band statistics and control information for an RTP session. It partners with RTP in the delivery and packaging of multimedia data, but does not transport any media data itself. |
||
RTOS |
|
A real-time operating system (RTOS) is an operating system (OS) intended to serve real-time applications that process data as it comes in, typically without buffer delays. Processing time requirements (including any OS delay) are measured in tenths of seconds or shorter increments of time. A real time system is a time bound system which has well defined fixed time constraints. Processing must be done within the defined constraints or the system will fail. They either are event driven or time sharing. Event driven systems switch between tasks based on their priorities while time sharing systems switch the task based on clock interrupts. Most RTOS's use a pre-emptive scheduling algorithm. |
||
RTP |
Real-time Protocol |
The Real-time Transport Protocol (RTP) is a network protocol for delivering audio and video over IP networks. RTP is used extensively in communication and entertainment systems that involve streaming media, such as telephony, video teleconference applications including WebRTC, television services and web-based push-to-talk features. |
||
RTSP |
Real Time Streaming Protocol |
The Real Time Streaming Protocol (RTSP) is a network control protocol designed for use in entertainment and communications systems to control streaming media servers. The protocol is used for establishing and controlling media sessions between end points. Clients of media servers issue VCR-style commands, such as play, record and pause, to facilitate real-time control of the media streaming from the server to a client (Video On Demand) or from a client to the server (Voice Recording). |
||
Ruby |
|
Ruby is a dynamic, interpreted, reflective, object-oriented, general-purpose programming language. It was designed and developed in the mid-1990s by Yukihiro "Matz" Matsumoto in Japan. |
||
Ruby on rails |
|
Ruby on Rails, or Rails, is a server-side web application framework written in Ruby under the MIT License. Rails is a model–view–controller (MVC) framework, providing default structures for a database, a web service, and web pages. It encourages and facilitates the use of web standards such as JSON or XML for data transfer, and HTML, CSS and JavaScript for display and user interfacing. In addition to MVC, Rails emphasizes the use of other well-known software engineering patterns and paradigms, including convention over configuration (CoC), don't repeat yourself (DRY), and the active record pattern. |
||
Rule of Simplicity |
|
Rules of Simplicity is a set of criteria, in priority order, proposed by Kent Beck to judge whether some source code is "simple enough." |
||
RUP |
Rational Unified Process |
an object-oriented and Web-enabled program development methodology that is said to be like an online mentor that provides guidelines, templates, and examples for all aspects and stages of program development. |