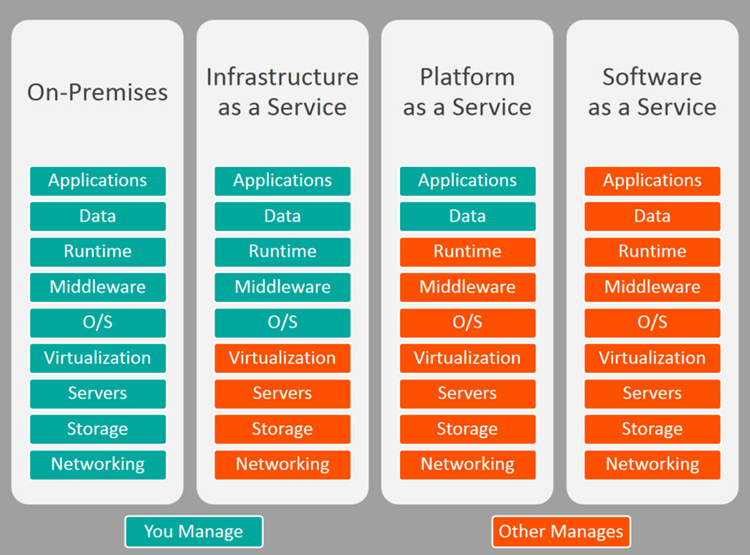
PaaS | Platform As A Service | Platform as a Service (PaaS) or Application Platform as a Service (aPaaS) or platform-based service is a category of cloud computing services that provides a platform allowing customers to develop, run, and manage applications without the complexity of building and maintaining the infrastructure typically associated with developing and launching an app
|
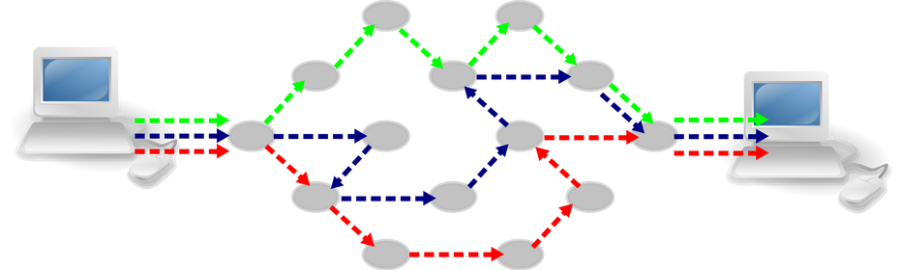
packet sniffing | A packet analyzer (also known as a packet sniffer) is a computer program or piece of computer hardware (such as a packet capture appliance) that can intercept and log traffic that passes over a digital network or part of a network. Packet capture is the process of intercepting and logging traffic. As data streams flow across the network, the sniffer captures each packet and, if needed, decodes the packet's raw data, showing the values of various fields in the packet, and analyzes its content according to the appropriate RFC or other specifications. | |
Packet Switched | Packet switching is a method of grouping data which is transmitted over a digital network into packets which are made of a header and a payload. Data in the header is used by networking hardware to direct the packet to its destination where the payload is extracted and used by application software. Packet switching is the primary basis for data communications in computer networks worldwide. | |
PAF | Postal Address File | Royal Mail Postal Address File data |
Pair Programming | Pair programming consists of two programmers sharing a single workstation (one screen, keyboard and mouse among the pair). | |
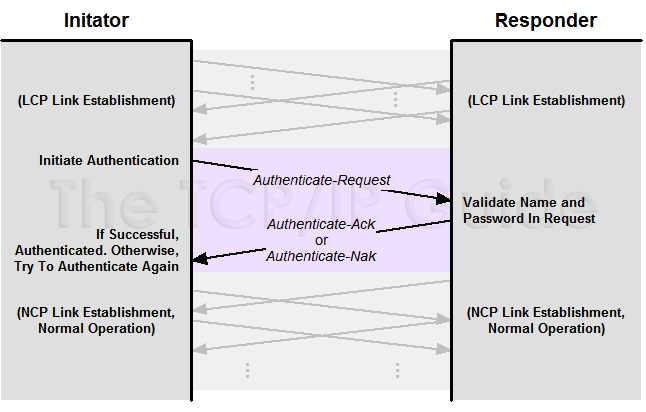
PAP | Password Authentication Protocol | Password Authentication Protocol (PAP) is a password-based authentication protocol used by Point to Point Protocol (PPP) to validate users. Almost all network operating system remote servers support PAP. |
Parametric Estimation | Estimation using an algorithmic model, normally as part of a software tool. Models work by taking input factors and calculating outputs with algorithms based on historical data. | |
Pascal | Pascal is an imperative and procedural programming language, which Niklaus Wirth designed in 1968–69 and published in 1970, as a small, efficient language intended to encourage good programming practices using structured programming and data structuring. It is named in honor of the French mathematician, philosopher and physicist Blaise Pascal. | |
Pattern | CxPattern | CxOne pattern material type. A predefined model or template used to create an artifact or accomplish a goal. See CxOneOverview for description. |
PCM | Pulse-code modulation | Pulse-code modulation (PCM) is a method used to digitally represent sampled analog signals. It is the standard form of digital audio in computers, compact discs, digital telephony and other digital audio applications. In a PCM stream, the amplitude of the analog signal is sampled regularly at uniform intervals, and each sample is quantized to the nearest value within a range of digital steps. |
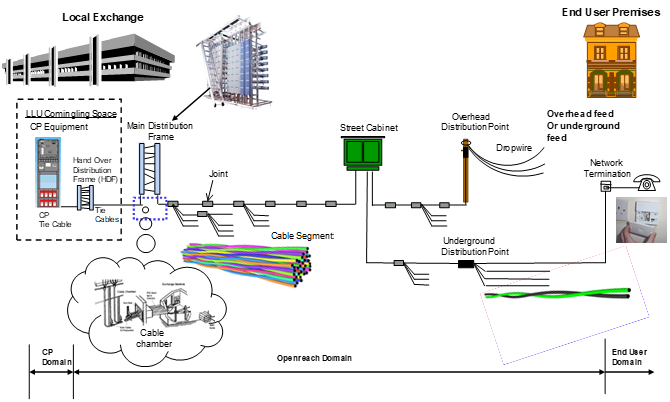
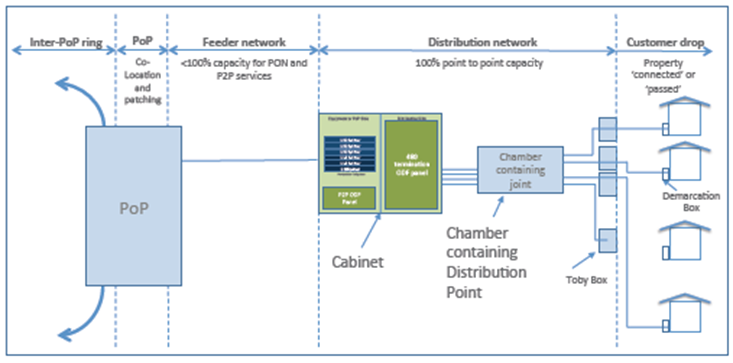
PCP | Primary Connection Point | Part of the line plant, in the form of a metal cabinet at the roadside, that enables flexibility between the main cables from the exchange and the smaller cables to individual streets or premises, also known as a Cabinet, or Cab" "Primary Cross-connection Point - this is the local street cabinet in which cables extending out to local distribution points are aggregated and connected to larger copper and fibre optic cables to move the voice and data signals to and from the local exchange |
PCRF | Policy and Charging Rules Function | Policy and Charging Rules Function (PCRF) is the software node designated in real-time to determine policy rules in a multimedia network. As a policy tool, the PCRF plays a central role in next-generation networks. Unlike earlier policy engines that were added onto an existing network to enforce policy, the PCRF is a software component that operates at the network core and accesses subscriber databases and other specialized functions, such as a charging system, in a centralized manner. Because it operates in real time, the PCRF has an increased strategic significance and broader potential role than traditional policy engines. This has led to a proliferation of PCRF products since 2008. |
PCS | Physical Coding Sub-layer | The Physical Coding Sublayer (PCS) is a networking protocol sublayer in the Fast Ethernet, Gigabit Ethernet, and 10 Gigabit Ethernet standards. It resides at the top of the physical layer (PHY), and provides an interface between the Physical Medium Attachment (PMA) sublayer and the Media Independent Interface (MII). It is responsible for data encoding and decoding, scrambling and descrambling, alignment marker insertion and removal, block and symbol redistribution, and lane block synchronization and deskew. |
PDCP | Packet Data Convergence Protocol | PDCP is an abbreviation for Packet Data Convergence Protocol. This protocol is specified by 3GPP in TS 25.323 for UMTS, TS 36.323 for LTE and TS 38.323 for 5G New Radio [NR). The PDCP is located in the Radio Protocol Stack in the UMTS/LTE/5G Air interface on top of the RLC layer. |
PDH | plesiochronous digital hierarchy | The plesiochronous digital hierarchy (PDH) is a technology used in telecommunications networks to transport large quantities of data over digital transport equipment such as fibre optic and microwave radio systems. The term plesiochronous is derived from Greek plēsios, meaning near, and chronos, time, and refers to the fact that PDH networks run in a state where different parts of the network are nearly, but not quite perfectly, synchronized. |
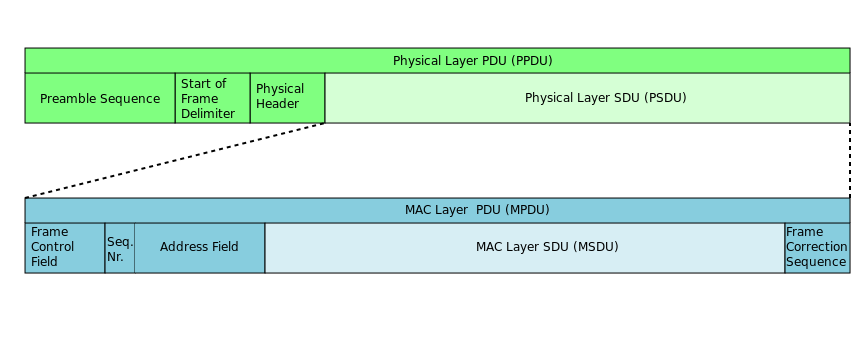
PDU | Protocol Data Unit | In telecommunications, a protocol data unit (PDU) is information that is transmitted as a single unit among peer entities of a computer network. A PDU may contain user data or control information and network addressing. In layered architectures of communication protocol stacks, each layer implements protocols tailored to the specific type or mode of data exchange, or network function of the layer. For example, the Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) implements a connection-oriented transfer mode, and the PDU of this protocol is called a segment, while the User Datagram Protocol (UDP) uses datagrams as protocol data unit for connection-less transfer. A layer lower in the Internet Protocol Suite, at the Internet Layer, the PDU is called a packet, irrespective of its payload type. |
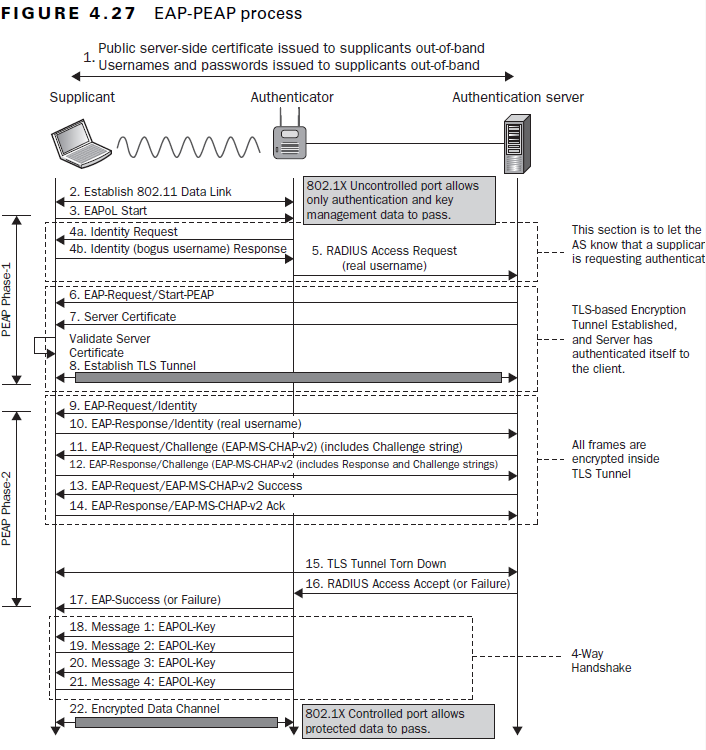
PEAP | Protected Extensible Authentication Protocol | The Protected Extensible Authentication Protocol, also known as Protected EAP or simply PEAP, is a protocol that encapsulates the Extensible Authentication Protocol (EAP) within an encrypted and authenticated Transport Layer Security (TLS) tunnel. The purpose was to correct deficiencies in EAP; EAP assumed a protected communication channel, such as that provided by physical security, so facilities for protection of the EAP conversation were not provided. |
peer review | a process used for checking the work performed by one's equals (peers) to ensure it meets specific criteria. | |
Pen testing | Penetration Testing | A penetration test, colloquially known as a pen test, is an authorized simulated attack on a computer system, performed to evaluate the security of the system. The test is performed to identify both weaknesses (also referred to as vulnerabilities), including the potential for unauthorized parties to gain access to the system's features and data, as well as strengths, enabling a full risk assessment to be completed. |
PER | Packed Encoding Rules | Packed Encoding Rules (PER) are ASN.1 encoding rules for producing a compact transfer syntax for data structures described in ASN.1, defined in 1994. |
Performance | May be used to describe the combination of feature and quality a system has (or that a project delivers). | |
Perl | Perl is a family of two high-level, general-purpose, interpreted, dynamic programming languages, Perl 5 and Perl 6. | |
Personas | Personas are synthetic biographies of fictitious users of the future product. | |
Perspective | During an inspection, an assigned focus used to increase the likelihood that each inspector will find unique issues or to focus attention an particular aspects of an artifact. | |
PERT chart | The program (or project) evaluation and review technique, commonly abbreviated PERT, is a statistical tool, used in project management, which was designed to analyze and represent the tasks involved in completing a given project. | |
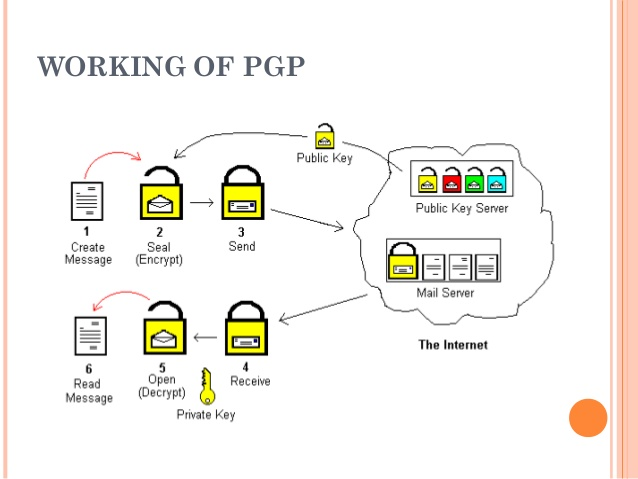
PGP | Pretty Good Privacy | Pretty Good Privacy (PGP) is an encryption program that provides cryptographic privacy and authentication for data communication. PGP is used for signing, encrypting, and decrypting texts, e-mails, files, directories, and whole disk partitions and to increase the security of e-mail communications. Phil Zimmermann developed PGP in 1991. |
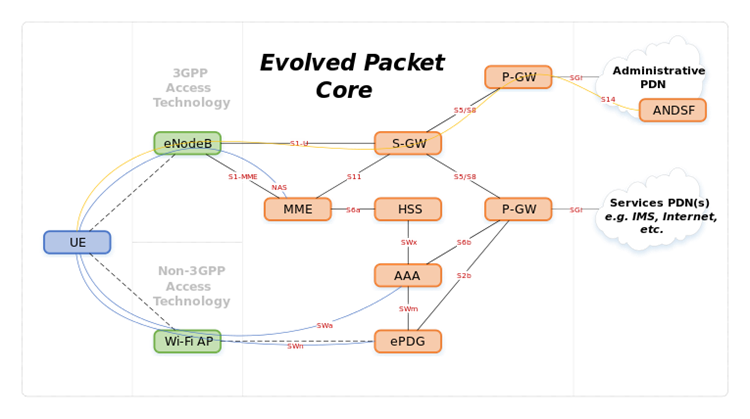
PGW | Packet Data Network Gateway | The PDN Gateway provides connectivity from the UE to external packet data networks by being the point of exit and entry of traffic for the UE. A UE may have simultaneous connectivity with more than one PGW for accessing multiple PDNs. The PGW performs policy enforcement, packet filtering for each user, charging support, lawful interception and packet screening. Another key role of the PGW is to act as the anchor for mobility between 3GPP and non-3GPP technologies such as WiMAX and 3GPP2 (CDMA 1X and EvDO).
|
Phase | A translation of a group of activities onto a portion of a lifecycle or a period of time defined by a schedule. Often used in conjunction with denoting a major transition in project activities or lifecycle processes. | |
Phased Estimation | The practice of creating estimates throughout a project's lifecycle, utilizing groups of estimation techniques optimized for each lifecycle phase. | |
PHP | PHP: Hypertext Preprocessor (or simply PHP) is a server-side scripting language designed for Web development, but also used as a general-purpose programming language. It was originally created by Rasmus Lerdorf in 1994, the PHP reference implementation is now produced by The PHP Group.[6] PHP originally stood for Personal Home Page, but it now stands for the recursive acronym PHP: Hypertext Preprocessor. | |
Planning and Tracking Lead | PTL | Directs overall flow of technical work on the project. Directly responsible for project planning and overseeing the execution of work breakdown, estimation, scheduling, and tracking. |
Planning Poker | An approach to estimation used by Agile teams. Each team member "plays" a card bearing a numerical value corresponding to a point estimation for a user story. | |
PLL | Phase Locked Loop | A phase-locked loop or phase lock loop abbreviated as PLL is a control system that generates an output signal whose phase is related to the phase of an input signal. There are several different types; the simplest is an electronic circuit consisting of a variable frequency oscillator and a phase detector in a feedback loop. The oscillator generates a periodic signal, and the phase detector compares the phase of that signal with the phase of the input periodic signal, adjusting the oscillator to keep the phases matched. |
PNT | Pointer data | OSNI Pointer data |
Points | (estimates in) Agile teams generally prefer to express estimates in units other than the time-honored "man-hours." Possibly the most widespread unit is "story points." | |
polymorphism | from the Greek meaning "having multiple forms," the characteristic of being able to assign a different meaning or usage to something in different contexts - specifically, to allow an entity such as a variable, a function, or an object to have more than one form. | |
POP | Point Of Presence | A point of presence (PoP) is an artificial demarcation point or interface point between communicating entities. |
portability | a characteristic attributed to a computer program if it can be used in an operating systems other than the one in which it was created without requiring major rework. | |
POSIX | The Portable Operating System Interface (POSIX) is a family of standards specified by the IEEE Computer Society for maintaining compatibility between operating systems. POSIX defines the application programming interface (API), along with command line shells and utility interfaces, for software compatibility with variants of Unix and other operating systems. | |
Postmortem | A phase at the end of a software project during which project team members evaluate the project and learn lessons that can be applied to the next project. "Postmortem" also refers to the report created during the postmortem phase. | |
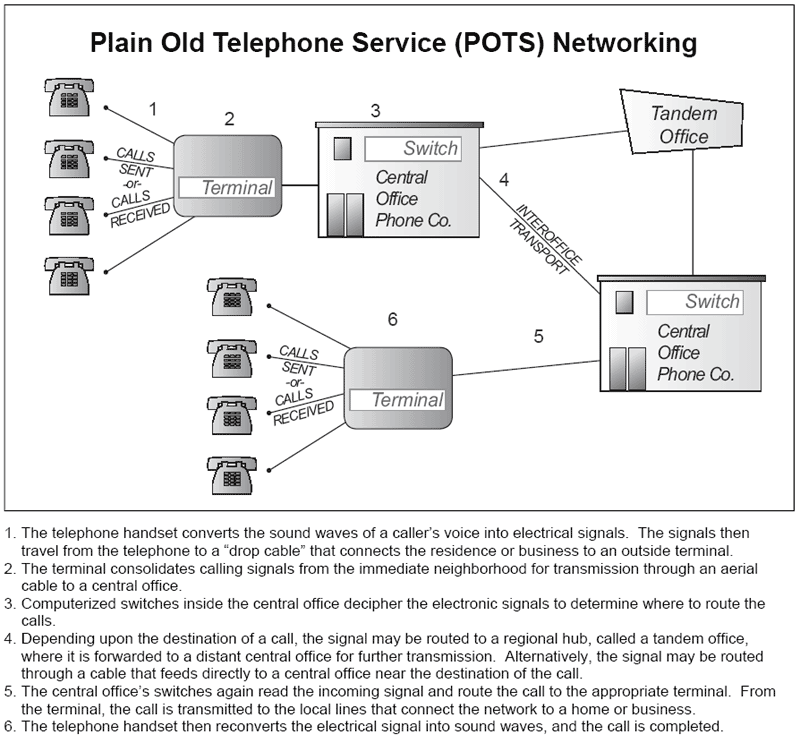
POTS | Plain Old Telephone Service or | POTS is a retronym for voice-grade telephone service employing analog signal transmission over copper loops |
PPP | Point-to-Point Protocol | In computer networking, Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP) is a data link layer (layer 2) communications protocol used to establish a direct connection between two nodes. It connects two routers directly without any host or any other networking device in between. It can provide connection authentication, transmission encryption,[1] and compression. |
PPPoE | PPP over Ethernet | The Point-to-Point Protocol over Ethernet (PPPoE) is a network protocol for encapsulating PPP frames inside Ethernet frames. It appeared in 1999, in the context of the boom of DSL as the solution for tunneling packets over the DSL connection to the ISP's IP network, and from there to the rest of the Internet. A 2005 networking book noted that "Most DSL providers use PPPoE, which provides authentication, encryption, and compression." Typical use of PPPoE involves leveraging the PPP facilities for authenticating the user with a username and password, predominately via the PAP protocol and less often via CHAP. |
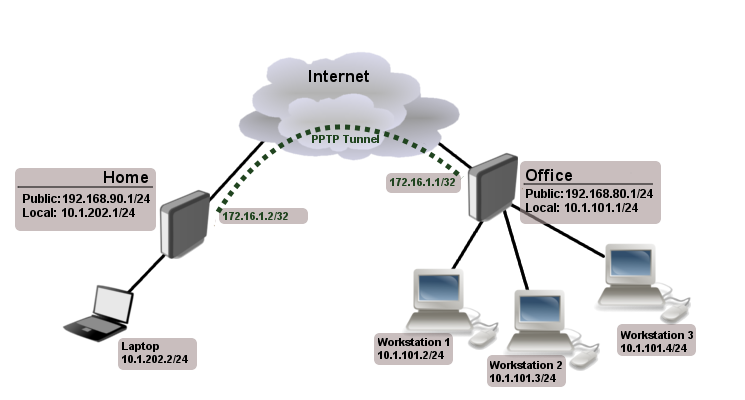
PPTP | Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol | The Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol (PPTP) is an obsolete method for implementing virtual private networks, with many known security issues. PPTP uses a TCP control channel and a Generic Routing Encapsulation tunnel to encapsulate PPP packets. |
Preemption | In computing, preemption is the act of temporarily interrupting a task being carried out by a computer system, without requiring its cooperation, and with the intention of resuming the task at a later time. Such changes of the executed task are known as context switches. It is normally carried out by a privileged task or part of the system known as a preemptive scheduler, which has the power to preempt, or interrupt, and later resume, other tasks in the system. | |
Preview | An engineering discussion where materials have been prepared ahead of time for review and discussion in a meeting. The goal is to probe proposed solution to detect defects and suggest alternatives. | |
PRINCE2 | a project management methodology developed by the government of the United Kingdom that makes use of the best proven practices from a variety of industries and backgrounds. | |
Process | A standard method for performing an activity or task. | |
Process Flow | A process model which defines the materials, structure, techniques, actions, events, and other elements necessary to implement a lifecycle, workflow, or methodology. | |
Product Owner | The product owner is a role created by the Scrum Framework responsible for making sure the team delivers the desired outcome. | |
Product Release | A release that is produced for distribution and/or deployment to end users. | |
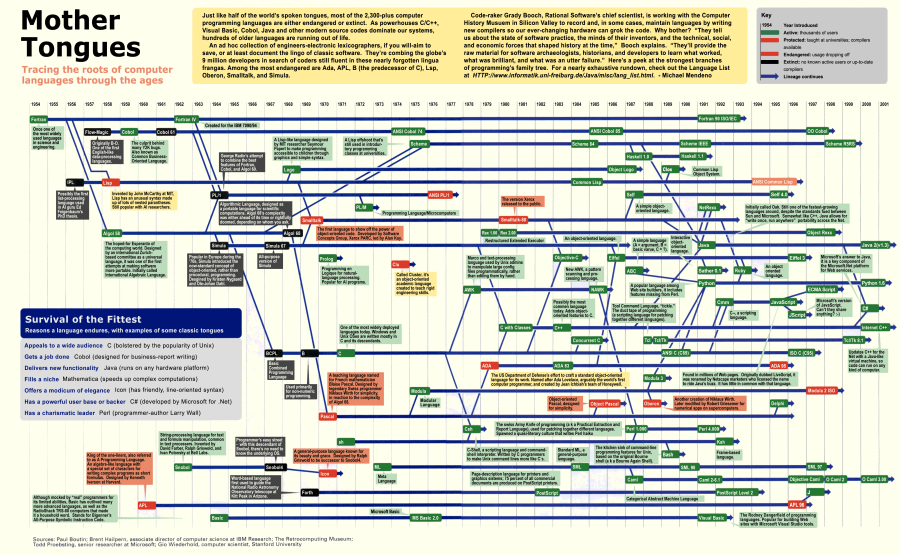
programming language | A programming language is a formal language which comprises a set of instructions used to produce various kinds of output. Programming languages are used to create programs that implement specific algorithms. | |
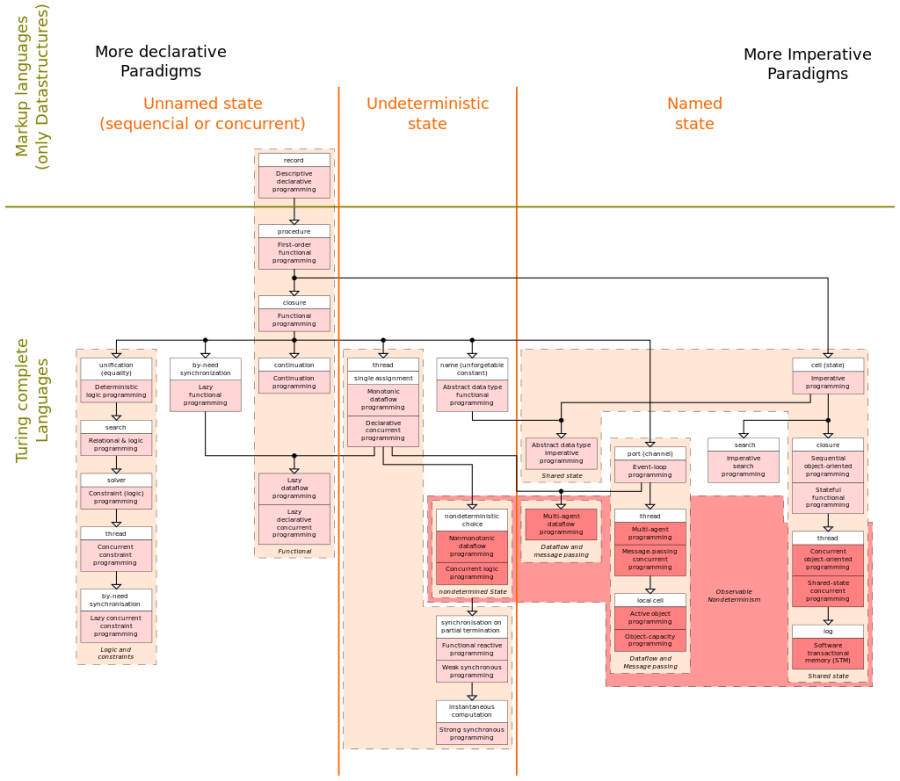
Programming paradigm | Programming paradigms are a way to classify programming languages based on their features. Languages can be classified into multiple paradigms.
| |
Progressive Elaboration | PMBOK term for iteratively defining a project's requirements, moving from the general to the specific as the project is underway. Most software lifecycles and projects employ some degree of progressive elaboration. Relates to project headlights and rolling wave planning. | |
Project | A temporary endeavor undertaken to create a unique product or service. Normally used with CxOne to refer to a project creating a software system. | |
Project Build | PB | Build performed as part of a shared project build process, usually in a dedicated build environment. Compare to local build. |
Project Business Manager | PBM | Responsible for successful business outcome of the project. In charge of project staffing, acquiring resources for the project, personnel issues, top-level work assignments, and client interaction. Is the top decision maker on the project, but normally defers technical decisions to the appropriate technical lead. |
Project Charter | Used to incept and define a project. Documents the objectives, business case, risks and assets, resources, and constraints of a project. | |
Project Chartering | A high-level summary of the project's key success factors displayed on one wall of the team room as a flipchart-sized sheet of paper. | |
Project Estimate | An estimate that characterizes work on an entire project or large portion of a project. Project estimates are often the result of significant effort to predict a large phase of a project, and utilize several different techniques. Compare to task estimate. | |
Project Headlights | The concept that there is a sliding window of time that a project's plan can be clearly defined with confidence. Beyond this "lighted" area, project planning is less precise and entails more uncertainty. Derives from the phrase "don't drive beyond your headlights". | |
Project History | Summarizes the significant information and statistics about an entire project. | |
Project Log | Describes significant information and statistics about each phase of a project. | |
Project Management | PM | The act of managing a project, including planning, tracking, control, and reporting activities. |
Project Management Body of Knowledge | PMBOK | PMI developed definition of the essential knowledge related to the science and discipline of project management. |
Project Management Institute | PMI | Professional organization for project managers. Developers of the PMBOK. |
Project Manager | PM | Often used as synonym for project business manager, especially when one person is playing both project business manager and planning and tracking lead roles. Also used to refer generically to an individual playing a management role on a project. |
Project Plan | PP | The controlling document for a project that defines how the project will be executed. |
Project Reviewer | Performs reviews and audits on projects using personnel who are not participating on the project. Ensures processes are being followed and risks are being identified and managed. | |
Project Sponsor | Individual or entity responsible for sponsoring a project. Synonym for authority in a project charter. Initiates and staffs a project, directly oversees the project business manager. Ensures that the project is meeting the technical and business needs of external and internal stakeholders. | |
pseudocode | a detailed yet readable description of what a computer program or algorithm must do, expressed in a formally-styled natural language rather than in a programming language. | |
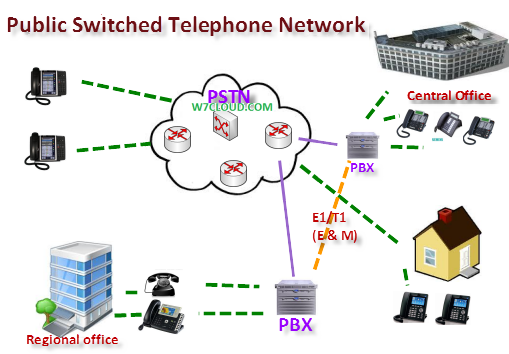
PSTN | Public Switched Telephone Network | The public switched telephone network (PSTN) is the aggregate of the world's circuit-switched telephone networks that are operated by national, regional, or local telephony operators, providing infrastructure and services for public telecommunication. |
PTP | Precision Time Protocol | The Precision Time Protocol (PTP) is a protocol used to synchronize clocks throughout a computer network. On a local area network, it achieves clock accuracy in the sub-microsecond range, making it suitable for measurement and control systems. |
PTT | Push-to-talk | Push-to-talk (PTT), also known as press-to-transmit, is a method of having conversations or talking on half-duplex communication lines, including two-way radio, using a momentary button to switch from voice reception mode to transmit mode. |
PVC | Permanent Virtual Circuit | A permanent virtual circuit (PVC) is a virtual circuit established for repeated/continuous use between the same DTE. In a PVC, the long-term association is identical to the data transfer phase of a virtual call. Permanent virtual circuits eliminate the need for repeated call set-up and clearing. Frame relay is typically used to provide PVCs. |
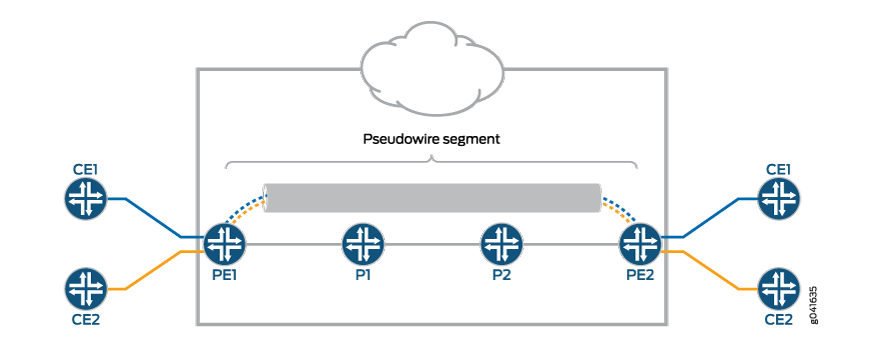
PW | PseudoWire | A pseudowire (or pseudo-wire) is an emulation of a point-to-point connection over a packet-switching network |
PWFQ | Priority-based Weighted Fair Queueing | See WFQ |
Python (2.x & 3.x) | Python is an interpreted high-level programming language for general-purpose programming. Created by Guido van Rossum and first released in 1991, Python has a design philosophy that emphasizes code readability, notably using significant whitespace. It provides constructs that enable clear programming on both small and large scales. In July 2018, the creator Van Rossum stepped down as the leader in the language community after 30 years. |