Objective C |
|
Objective-C is a general-purpose, object-oriented programming language that adds Smalltalk-style messaging to the C programming language. It was the main programming language used by Apple for the OS X and iOS operating systems, and their respective application programming interfaces (APIs) Cocoa and Cocoa Touch prior to the introduction of Swift. |
Objectives |
|
Synonym for goals. |
ODF |
Optical Distribution Frame |
In telecommunications, a distribution frame is a passive device which terminates cables, allowing arbitrary interconnections to be made. |
OFC |
Optical fiber connector |
An optical fiber connector terminates the end of an optical fiber, and enables quicker connection and disconnection than splicing. The connectors mechanically couple and align the cores of fibers so light can pass. Better connectors lose very little light due to reflection or misalignment of the fibers. In all, about 100 different types of fiber optic connectors have been introduced to the market. |
Ofcom |
|
The Office of Communications, commonly known as Ofcom, is the UK government-approved regulatory and competition authority for the broadcasting, telecommunications and postal industries of the United Kingdom. |
OFDMA |
Orthogonal frequency-division multiple access |
Orthogonal frequency-division multiple access (OFDMA) is a multi-user version of the popular orthogonal frequency-division multiplexing (OFDM) digital modulation scheme. Multiple access is achieved in OFDMA by assigning subsets of subcarriers to individual users. This allows simultaneous low-data-rate transmission from several users |
OO |
Object-oriented |
Object-oriented programming (OOP) is a programming paradigm based on the concept of "objects", which may contain data, in the form of fields, often known as attributes; and code, in the form of procedures, often known as methods. A feature of objects is that an object's procedures can access and often modify the data fields of the object with which they are associated (objects have a notion of "this" or "self"). In OOP, computer programs are designed by making them out of objects that interact with one another. There is significant diversity of OOP languages, but the most popular ones are class-based, meaning that objects are instances of classes, which typically also determine their type. |
Operations Plan |
|
A plan specifying how a system will be utilized after deployment along with other information such as roles, responsibilities, maintenance schedules, etc. |
OPUS |
|
Opus is a lossy audio coding format developed by the Xiph.Org Foundation and standardized by the Internet Engineering Task Force, designed to efficiently code speech and general audio in a single format, while remaining low-latency enough for real-time interactive communication and low-complexity enough for low-end embedded processors. Opus replaces both Vorbis and Speex for new applications, and several blind listening tests have ranked it higher-quality than any other standard audio format at any given bitrate until transparency is reached, including MP3, AAC, and HE-AAC. |
OS X |
|
macOS (previously Mac OS X and later OS X) is a series of graphical operating systems developed and marketed by Apple Inc. since 2001. It is the primary operating system for Apple's Mac family of computers. Within the market of desktop, laptop and home computers, and by web usage, it is the second most widely used desktop OS, after Microsoft Windows. |
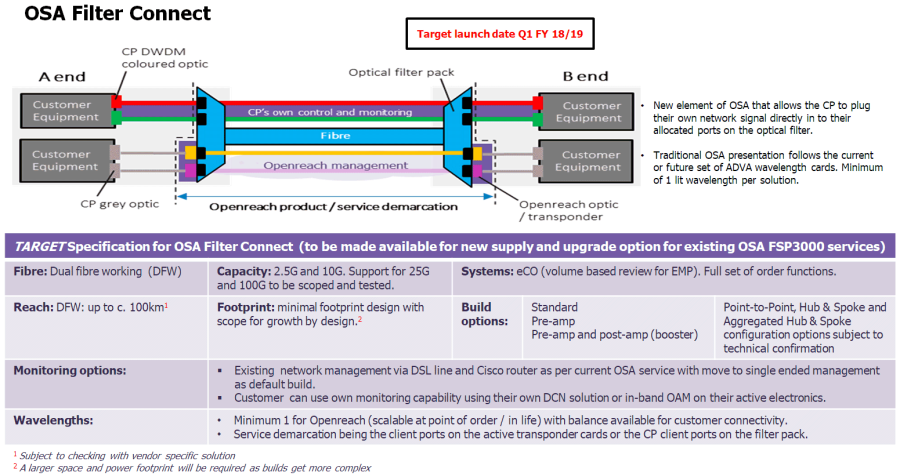
OSA-FC |
Optical Spectrum Access Filter Connect |
Openreach virtual dark fibre service that provides CPs all the key benefits of dark fibre – like the freedom to control and increase bandwidth usage at no extra cost – without compromising on service and maintenance levels. |
OSPF |
Open Shortest Path First |
Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) is a routing protocol for Internet Protocol (IP) networks. It uses a link state routing (LSR) algorithm and falls into the group of interior gateway protocols (IGPs), operating within a single autonomous system (AS). It is defined as OSPF Version 2 in RFC 2328 (1998) for IPv4. The updates for IPv6 are specified as OSPF Version 3 in RFC 5340 (2008). OSPF supports the Classless Inter-Domain Routing (CIDR) addressing model. |
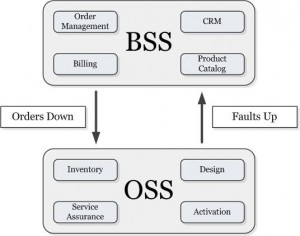
OSS |
Operations support systems |
Operations support systems (OSS), or operational support systems in British usage, are computer systems used by telecommunications service providers to manage their networks (e.g., telephone networks). They support management functions such as network inventory, service provisioning, network configuration and fault management.
|
OTN |
Optical Transport Network |
ITU-T defines an Optical Transport Network (OTN) as a set of Optical Network Elements (ONE) connected by optical fiber links, able to provide functionality of transport, multiplexing, switching, management, supervision and survivability of optical channels carrying client signals. |
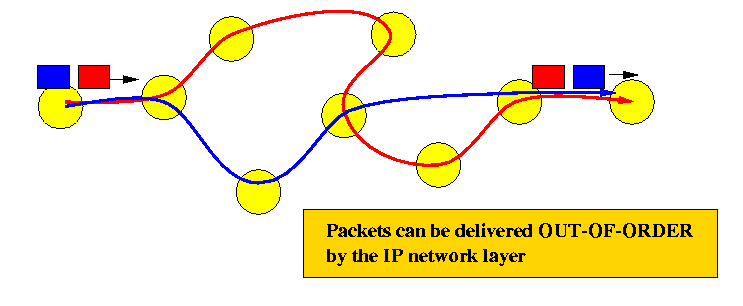
Out-of-order delivery |
|
In computer networking, out-of-order delivery is the delivery of data packets in a different order from which they were sent. Out-of-order delivery can be caused by packets following multiple paths through a network, or via parallel processing paths within network equipment that are not designed to ensure that packet ordering is preserved. One of the functions of TCP is to prevent the out-of-order delivery of data, either by reassembling packets into order or forcing retries of out-of-order packets. |
Overlap Dialling |
|
Overlap dialing is required by CAS signaled lines. Overlap dial provides for a longer time-out period between digits, also called the inter-digit timer. With overlap dial set to off, the gateway expects to receive the digits one right after the other coming in to this line with very little delay between digits. With overlap dial set to on, then the device waits up to about 2 seconds between digits. |