K & R |
Kernighan and Ritchie |
Brian Wilson Kernighan is a Canadian computer scientist who worked at Bell Labs alongside Unix creators Ken Thompson and Dennis Ritchie and contributed to the development of Unix. He is also coauthor of the AWK and AMPL programming languages. The "K" of K&R C and the "K" in AWK both stand for "Kernighan". |
K & R C |
|
In 1978, Brian Kernighan and Dennis Ritchie published the first edition of The C Programming Language. This book, known to C programmers as "K&R", served for many years as an informal specification of the language. The version of C that it describes is commonly referred to as K&R C. The second edition of the book covers the later ANSI C standard, described below. |
K & R indent style |
|
The K&R style is commonly used in C, C++, and other curly brace programming languages. Used in Kernighan and Ritchie's book The C Programming Language, it had its origins in Kernighan and Plauger's The Elements of Programming Style. |
Kanban |
|
a method for managing work, with an emphasis on just-in-time delivery. The Kanban Method is a means to design, manage and improve flow for knowledge work and allows teams to start where they are to drive evolutionary change. |
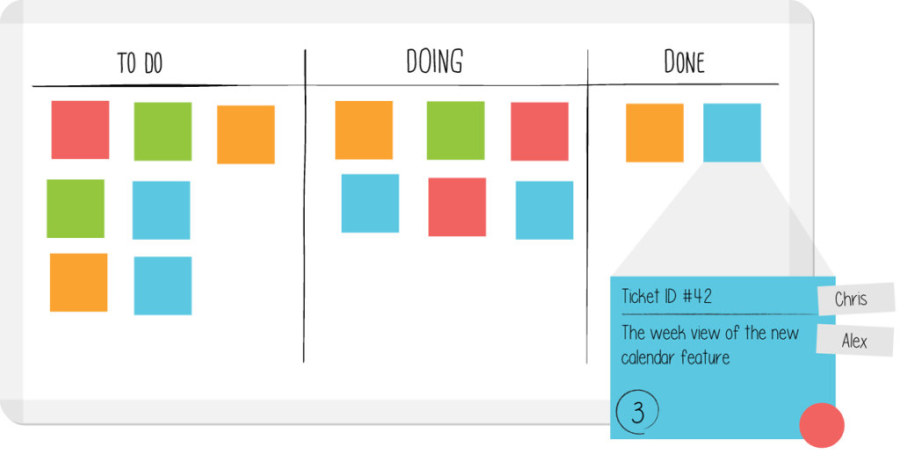
Kanban Board |
|
A Kanban Board is a visual workflow tool consisting of multiple columns. Each column represents a different stage in the workflow process. |
Kerberos |
|
Kerberos is a computer network authentication protocol that works on the basis of tickets to allow nodes communicating over a non-secure network to prove their identity to one another in a secure manner. The protocol was named after the character Kerberos (or Cerberus) from Greek mythology, the ferocious three-headed guard dog of Hades. Its designers aimed it primarily at a client–server model and it provides mutual authentication—both the user and the server verify each other's identity. Kerberos protocol messages are protected against eavesdropping and replay attacks. |
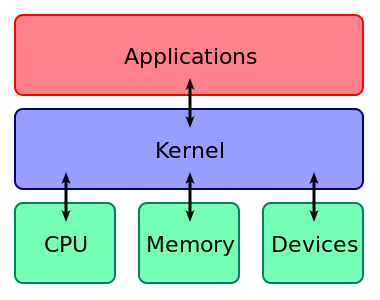
Kernel |
|
The kernel is a computer program that is the core of a computer's operating system, with complete control over everything in the system. On most systems, it is one of the first programs loaded on start-up (after the bootloader). It handles the rest of start-up as well as input/output requests from software, translating them into data-processing instructions for the central processing unit. It handles memory and peripherals like keyboards, monitors, printers, and speakers. |
KISS Principle |
Keep It Simple, Stupid |
the principle that people want products that are easy to learn and use, and that companies realize time and cost benefits by producing such products. |
Knowledge Management |
KM |
A mechanism or method of retaining, reusing, and providing people with useful and relevant information. |
KPI |
Key Performance Indicator |
A performance indicator or key performance indicator (KPI) is a type of performance measurement. KPIs evaluate the success of an organization or of a particular activity (such as projects, programs, products and other initiatives) in which it engages. |
ksh |
|
KornShell (ksh) is a Unix shell which was developed by David Korn at Bell Labs in the early 1980s and announced at USENIX on July 14, 1983. The initial development was based on Bourne shell source code. Other early contributors were Bell Labs developers Mike Veach and Pat Sullivan, who wrote the Emacs and vi-style line editing modes' code, respectively. KornShell is backward-compatible with the Bourne shell and includes many features of the C shell, inspired by the requests of Bell Labs users |