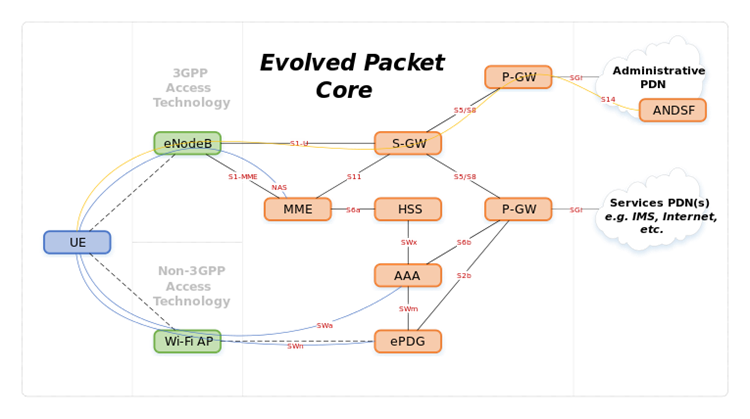
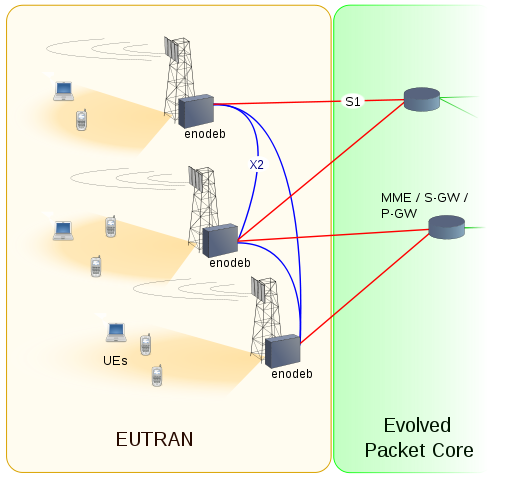
E NodeB | Evolved Node-B | E-UTRAN Node B, also known as Evolved Node B (abbreviated as eNodeB or eNB), is the element in E-UTRA of LTE that is the evolution of the element Node B in UTRA of UMTS. It is the hardware that is connected to the mobile phone network that communicates directly wirelessly with mobile handsets (UEs), like a base transceiver station (BTS) in GSM networks. |
E.164 | E.164 is an ITU-T recommendation, titled The international public telecommunication numbering plan, that defines a numbering plan for the worldwide public switched telephone network (PSTN) and some other data networks. | |
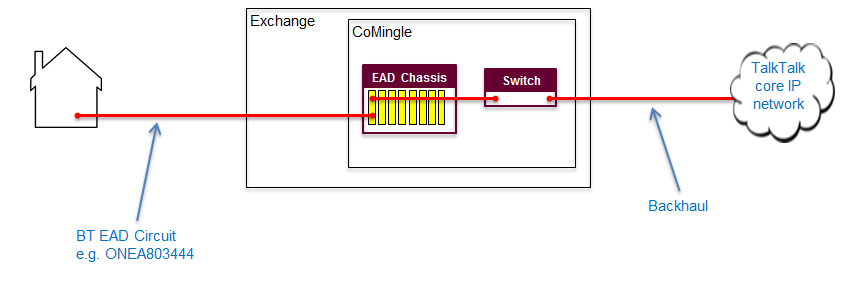
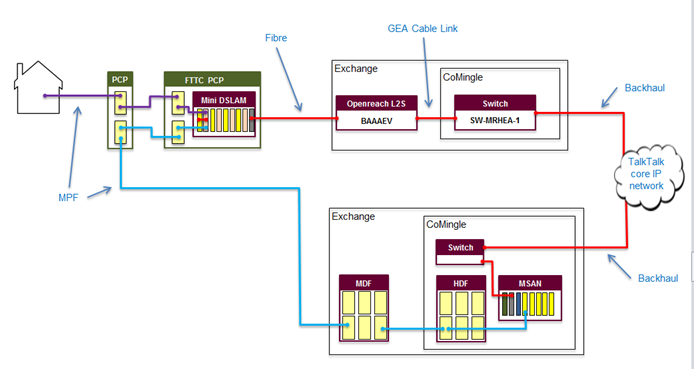
EAD | Ethernet Access Direct | Ethernet Access Direct (EAD) provides point-to-point data connectivity between sites. It can be used to build and extend customer networks, develop new infrastructure, and meet low-capacity backhaul requirements (ie up to 1Gbps, which is the starting bandwidth for Ethernet Backhaul Direct). EAD supports a range of requirements including cloud computing, simultaneous online pupil access in classrooms and storage area network connectivity. |
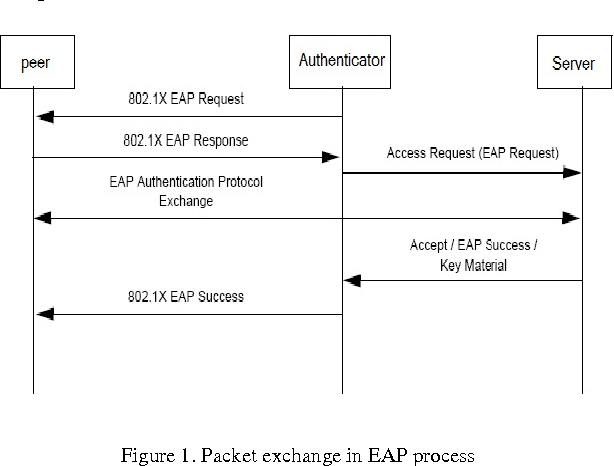
EAP | Extensible Authentication Protocol | Extensible Authentication Protocol, or EAP, is an authentication framework frequently used in wireless networks and point-to-point connections. It is defined in RFC 3748, which made RFC 2284 obsolete, and is updated by RFC 5247. |
Earned Value | EV | A scheduling technique for tracking variance of actual performance to planned performance. |
Earned Value Management | EVM | The act or discipline of managing projects utilizing earned value techniques and practices. |
Echo | In audio signal processing and acoustics, Echo is a reflection of sound that arrives at the listener with a delay after the direct sound. The delay is proportional to the distance of the reflecting surface from the source and the listener. Typical examples are the echo produced by the bottom of a well, by a building, or by the walls of an enclosed room and an empty room. A true echo is a single reflection of the sound source. | |
Echo cancellation | Echo suppression and echo cancellation are methods used in telephony to improve voice quality by preventing echo from being created or removing it after it is already present. In addition to improving subjective audio quality, echo suppression increases the capacity achieved through silence suppression by preventing echo from traveling across a network. Echo suppressors were developed in the 1950s in response to the first use of satellites for telecommunications, but they have since been largely supplanted by better performing echo cancellers.
| |
Echo Cancellation - G.168 | Echo has a major effect on voice quality in telecommunication networks. The objectionable effect of echo results from a combination of reflections from network components such as 2- to 4-wire converters, together with signal processing and transmission delay. Echo may cause users difficulty in | |
EDB | Emergency Database | |
EDGE | Enhanced Data rates for GSM Evolution | Enhanced Data rates for GSM Evolution (EDGE) (also known as Enhanced GPRS (EGPRS), or IMT Single Carrier (IMT-SC), or Enhanced Data rates for Global Evolution) is a digital mobile phone technology that allows improved data transmission rates as a backward-compatible extension of GSM. EDGE is considered a pre-3G radio technology and is part of ITU's 3G definition. EDGE was deployed on GSM networks beginning in 2003 – initially by Cingular (now AT&T) in the United States. |
Editor | For inspections, performs any necessary rework on artifacts. | |
EEE 802.1Qay | Provider Backbone Bridge Traffic Engineering (PBB-TE) is an approved telecommunications networking standard, IEEE 802.1Qay-2009. PBB-TE adapts Ethernet technology to carrier class transport networks. It is based on the layered VLAN tags and MAC-in-MAC encapsulation defined in IEEE 802.1ah (Provider Backbone Bridges (PBB)), but it differs from PBB in eliminating flooding, dynamically created forwarding tables, and spanning tree protocols. Compared to PBB and its predecessors, PBB-TE behaves more predictably and its behavior can be more easily controlled by the network operator, at the expense of requiring up-front connection configuration at each bridge along a forwarding path. PBB-TE Operations, Administration, and Management (OAM) is usually based on IEEE 802.1ag. It was initially based on Nortel's Provider Backbone Transport (PBT). | |
EFM | Ethernet in the First Mile | describes the inclusion of an Ethernet connection at any point in the network where the provider and customer are immediately connected. |
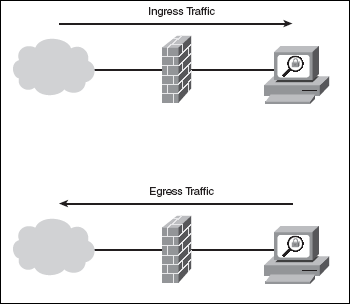
Egress | Egress traffic is network traffic that begins inside of a network and proceeds through its routers to a destination somewhere outside of the network. For example, an email message that is considered egress traffic will travel from a user's workstation and pass through the enterprise's LAN routers before it is delivered to the Internet to travel to its final destination. | |
EIA | Electronic Industries Alliance | The Electronic Industries Alliance (EIA; until 1997 Electronic Industries Association) was a standards and trade organization composed as an alliance of trade associations for electronics manufacturers in the United States. They developed standards to ensure the equipment of different manufacturers was compatible and interchangeable. The EIA ceased operations on February 11, 2011, but the former sectors continue to serve the constituencies of EIA |
EIGRP | Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol | Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (EIGRP) is an advanced distance-vector routing protocol that is used on a computer network for automating routing decisions and configuration. The protocol was designed by Cisco Systems as a proprietary protocol, available only on Cisco routers. Functionality of EIGRP was converted to an open standard in 2013[1] and was published with informational status as RFC 7868 in 2016. |
embedded systems programming | the programming of an embedded system in some device using the permitted programming interfaces provided by that system. | |
Engineering Discussion | A brainstorming meeting designed to frame an issue and seek solutions for it. | |
Engineering Management | EM | Software engineering management. Planning, staffing, tracking, and controlling execution of software projects, along with team and organizational management. Also denotes the engineering management CKA. See CxStand_EngineeringManagement for more information. |
Engineering Process | Software engineering process. Defining how software engineering activities occur. Also denotes the engineering process CKA. See CxStand_Process for more information. | |
EoFTTC | Ethernet over Fibre to the Cabinet | Ethernet over Fibre to the Cabinet (EoFTTC) is provided by copper from your business premises over the short distance to the green cabinets in the street. Unlike standard broadband where the copper then continues all the way to the exchange, Ethernet over Fibre to the Cabinet traffic travels across a shared fibre optic circuit to the exchange. The extra distance doesn't lead to ongoing degradation of performance, which allows access to up to 20Mbps symmetrical speed with the additional boost downstream making a total of 76Mbps downstream bandwidth. |
EoS | Ethernet Over SONET | Ethernet Over SDH (EoS or EoSDH) or Ethernet over SONET refers to a set of protocols which allow Ethernet traffic to be carried over synchronous digital hierarchy networks in an efficient and flexible way. The same functions are available using SONET. |
ePDG | Evolved Packet Data Gateway | The main function of the ePDG is to secure the data transmission with a UE connected to the EPC over an untrusted non-3GPP access. For this purpose, the ePDG acts as a termination node of IPsec tunnels established with the UE. |
Epic | An epic is a large user story. | |
EPWS | Ethernet Private Wire Service | |
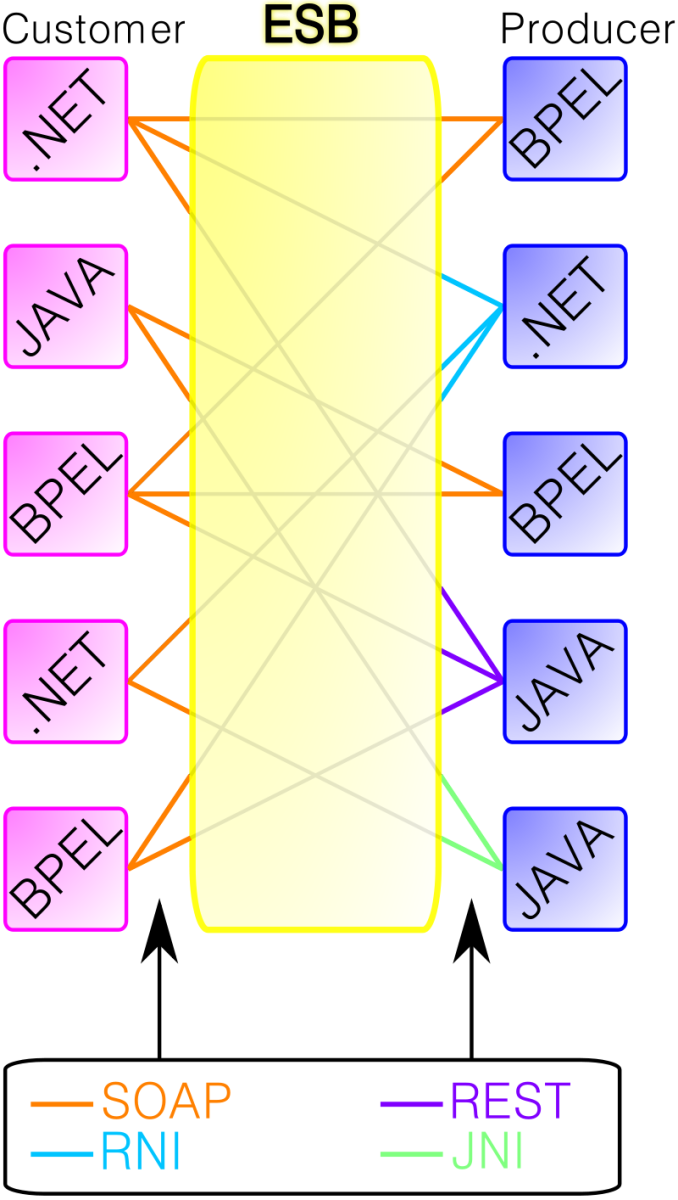
ESB | Enterprise Service Bus | An enterprise service bus (ESB) implements a communication system between mutually interacting software applications in a service-oriented architecture (SOA). It implements a software architecture as depicted in the picture. As it implements a distributed computing architecture, it implements a special variant of the more general client-server model, wherein, in general, any application using ESB can behave as server or client in turns. ESB promotes agility and flexibility with regard to high-level protocol communication between applications. The primary goal of the high-level protocol communication is enterprise application integration (EAI) of heterogeneous and complex service or application landscapes (a view from the network level).
|
Estimate | The output of an estimation process, containing a description of inputs, assumptions, methodology, and the resulting estimate values. Depending on purpose and formality an estimate's packaging can range from a document containing complete output of several different estimation techniques (see project estimate) to a terse summary (see task estimate). | |
Estimation | In software development, an "estimate" is the evaluation of the effort necessary to carry out a given development task; this is most often expressed in terms of duration. | |
Estimation | The process of determining the size, cost, schedule, effort, and/or quality estimates for a project. It is best to use as many different estimation techniques as possible when creating estimates, and to create estimates regularly through the life of a project. | |
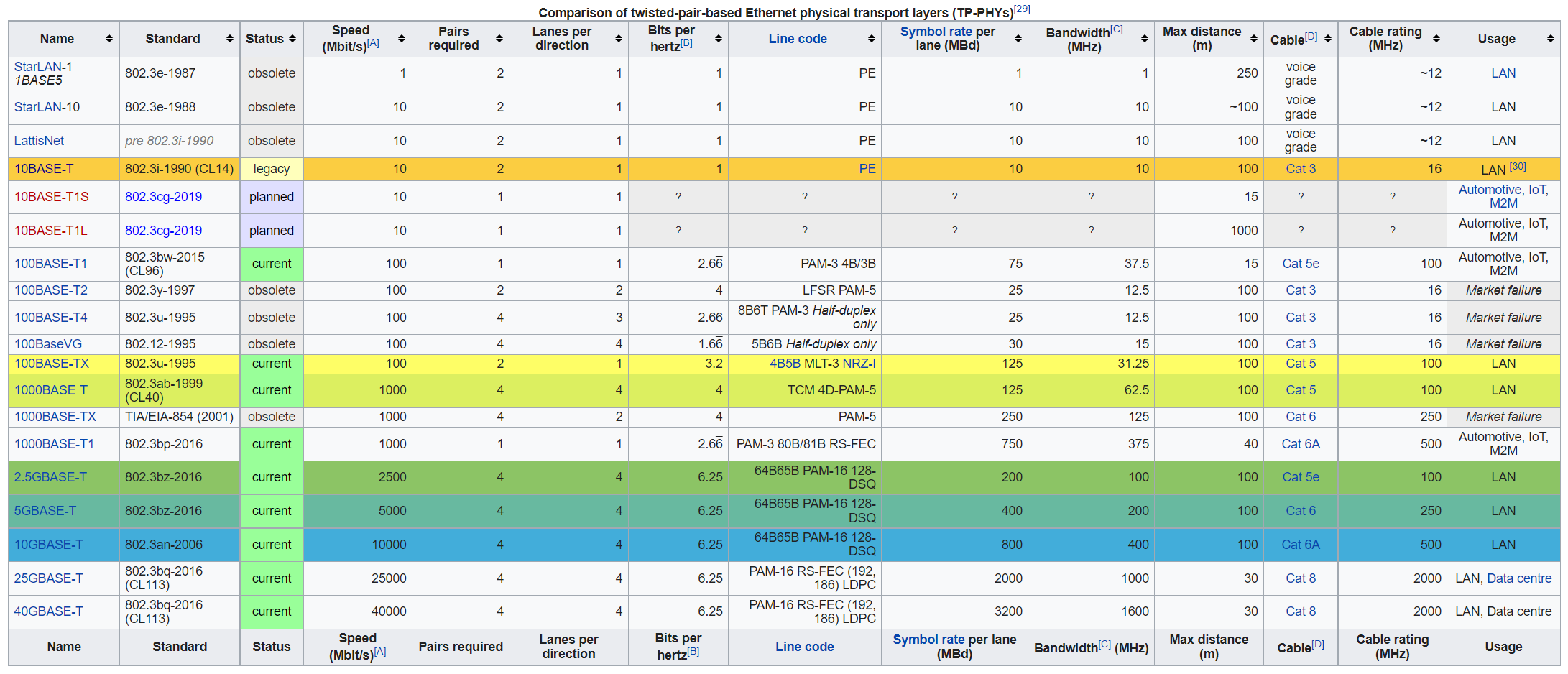
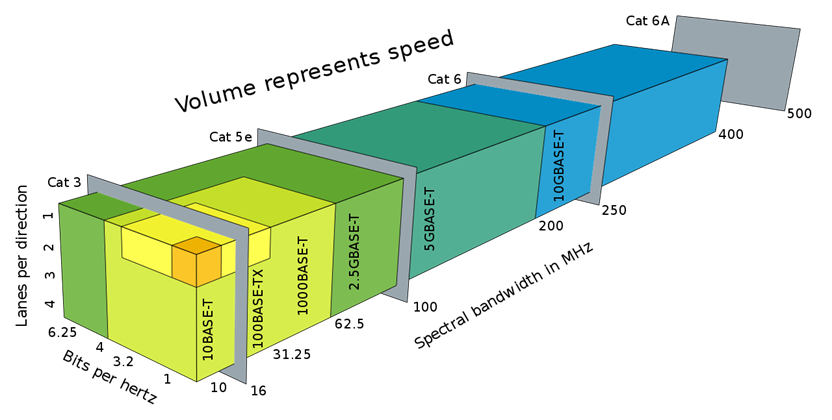
Ethernet over twisted pair | Ethernet over twisted-pair technologies use twisted-pair cables for the physical layer of an Ethernet computer network. They are a subset of all Ethernet physical layers. Early Ethernet used various grades of coaxial cable, but in 1984, StarLAN showed the potential of simple unshielded twisted pair. This led to the development of 10BASE-T and its successors 100BASE-TX, 1000BASE-T and 10GBASE-T, supporting speeds of 10 and 100 megabit per second, then 1 and 10 gigabit per second respectively. Two new variants of 10 megabit per second Ethernet over a single twisted pair, known as 10BASE-T1S and 10BASE-T1L, were standardized in IEEE Std 802.3cg-2019.[2] 10BASE-T1S has its origins in the automotive industry and may be useful in other short-distance applications where substantial electrical noise is present. 10BASE-T1L is a long-distance Ethernet, supporting connections up to 1 km in length. Both of these standards are finding applications implementing the Internet of things. | |
Ethical Hacking | The term "white hat" in Internet slang refers to an ethical computer hacker, or a computer security expert, who specializes in penetration testing and in other testing methodologies that ensures the security of an organization's information systems. Ethical hacking is a term meant to imply a broader category than just penetration testing. Contrasted with black hat, a malicious hacker, the name comes from Western films, where heroic and antagonistic cowboys might traditionally wear a white and a black hat respectively. | |
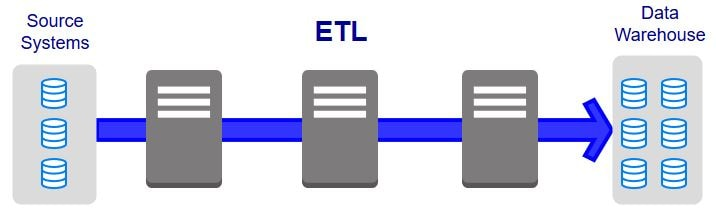
ETL | Extract, Transform, Load | ETL is short for extract, transform, load, three database functions that are combined into one tool to pull data out of one database and place it into another database.
|
ETSI | European Telecommunications Standards Institute | The European Telecommunications Standards Institute (ETSI) is an independent, not-for-profit, standardization organization in the telecommunications industry (equipment makers and network operators) in Europe, headquartered in Sophia-Antipolis, France, with worldwide projection. ETSI produces globally-applicable standards for Information and Communications Technologies (ICT), including fixed, mobile, radio, converged, broadcast and internet technologies. |
E-UTRAN | E-UTRA is the air interface of 3rd Generation Partnership Project (3GPP) Long Term Evolution (LTE) upgrade path for mobile networks. It is an acronym for Evolved Universal Mobile Telecommunications System (UMTS) Terrestrial Radio Access, also referred to as the 3GPP work item on the Long Term Evolution (LTE) also known as the Evolved Universal Terrestrial Radio Access (E-UTRA) in early drafts of the 3GPP LTE specification. E-UTRAN is the initialism of Evolved UMTS Terrestrial Radio Access Network and is the combination of E-UTRA, user equipment (UE), and E-UTRAN Node B or Evolved Node B (EnodeB). | |
Evaluation | CxEval | CxOne evaluation material type, see CxOneOverview for description. |
EVC | Ethernet Virtual Connection | Ethernet virtual circuits (EVCs) define a Layer 2 bridging architecture that supports Ethernet services. An EVC is defined by the Metro-Ethernet Forum (MEF) as an association between two or more user network interfaces that identifies a point-to-point or multipoint-to-multipoint path within the service provider network. An EVC is a conceptual service pipe within the service provider network. A bridge domain is a local broadcast domain that exists separately from VLANs. |
Evolutionary Delivery Lifecycle | A combination of the evolutionary prototyping and staged delivery lifecycles. | |
Evolutionary Prototyping Lifecycle | A system concept is evolved through iteration until the system is ready for delivery. | |
EVPL | Ethernet Virtual Private Line | Ethernet private line (EPL) and Ethernet virtual private line (EVPL) are data services defined by the MEF. EPL provides a point-to-point Ethernet virtual connection (EVC) between a pair of dedicated user–network interfaces (UNIs), with a high degree of transparency. EVPL provides a point-to-point or point-to-multipoint connection between a pair of UNIs. |
Expert Judgment | Estimation technique that relies on participants creating estimates based on personal experience and heuristics. | |
Explicit Change Control | Refers to artifacts managed directly by a change control board. Requirements and project plans are often under explicit change control. Compare to implicit change control. | |
Explicit Risk Management | Synonym for extrinsic risk management. | |
Exploratory Testing | Exploratory testing is, more than strictly speaking a "practice," a style or approach to testing software which is often contrasted to "scripted testing." | |
Extrinsic Risk Management | Formal risk management techniques that are added to a project or processes to explicitly mange risks. An example would be using a top 10 risks list to explicitly identify, prioritize, plan mitigation, and report outcome of risk management. Compare to intrinsic risk management. |
|