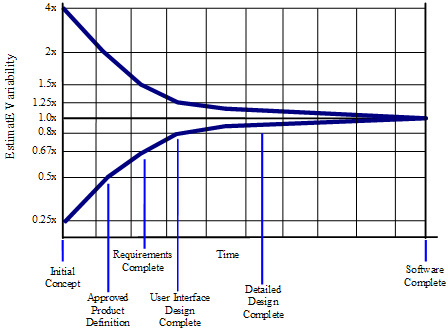
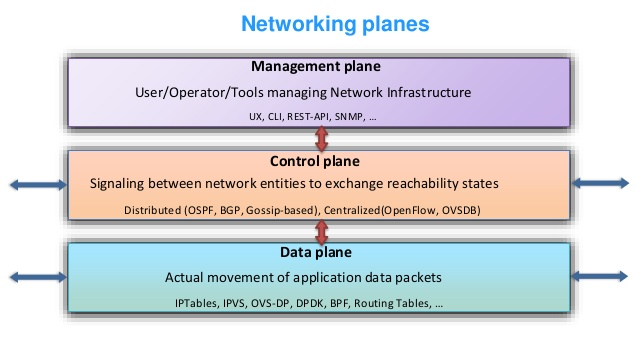
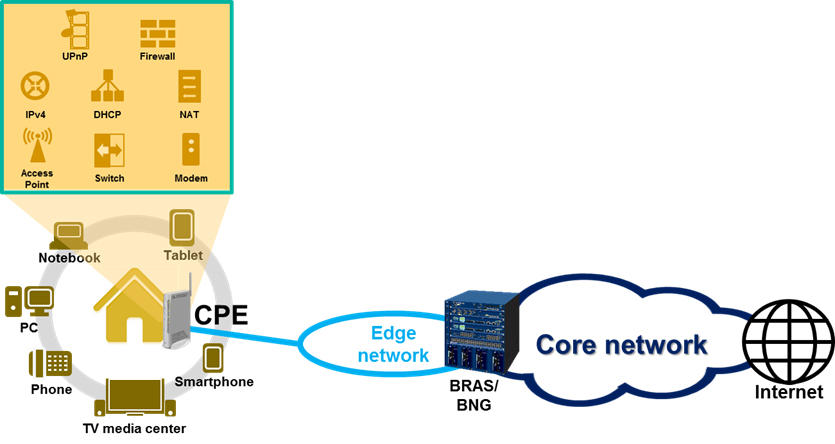
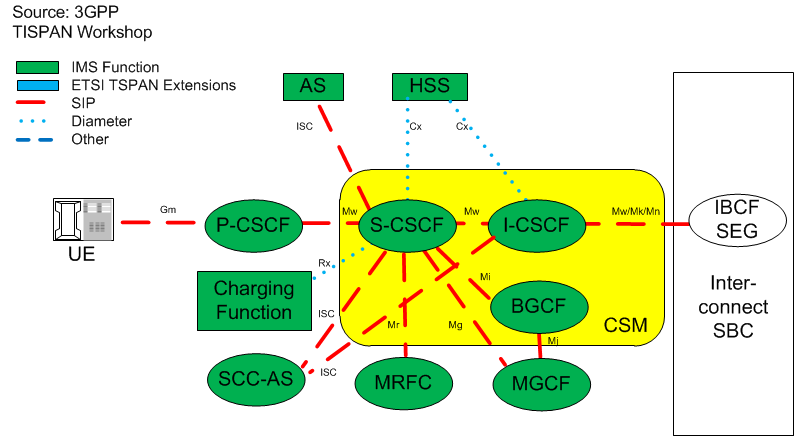
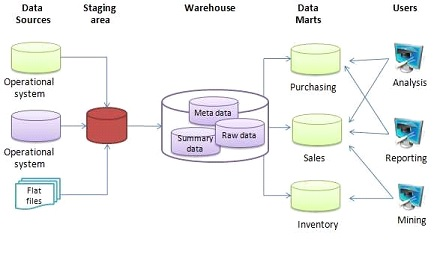
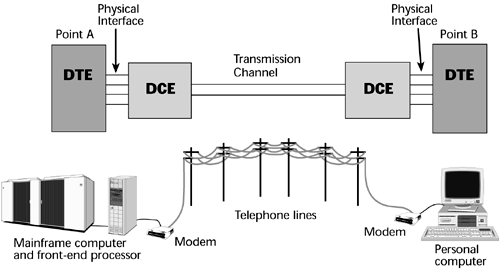
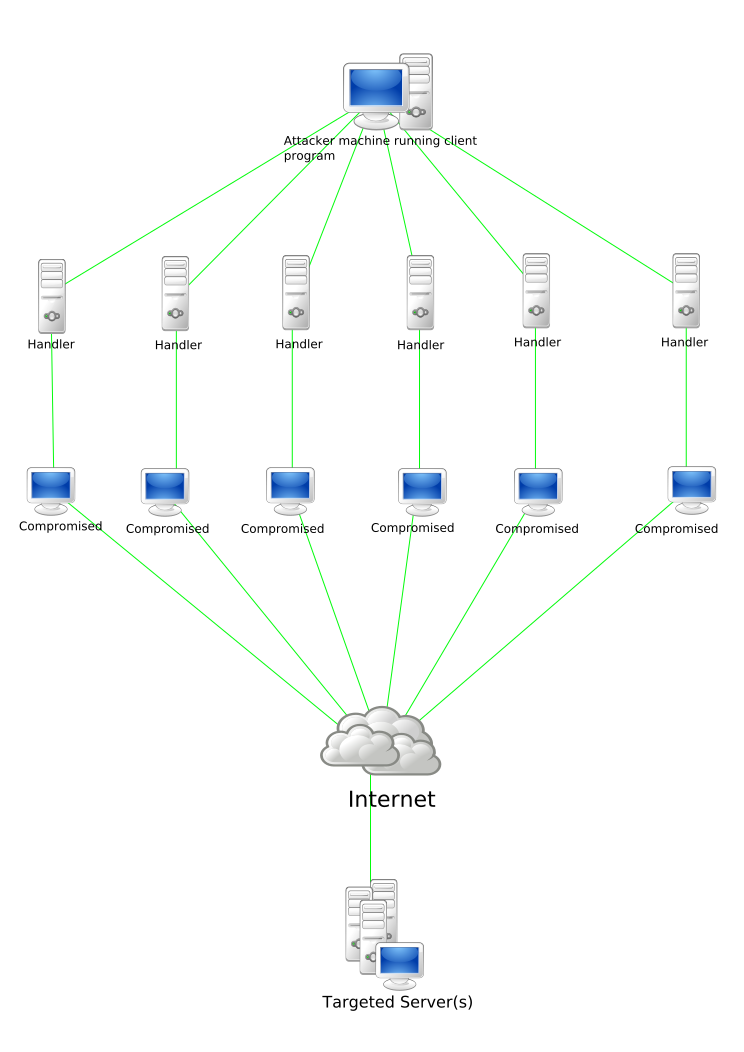
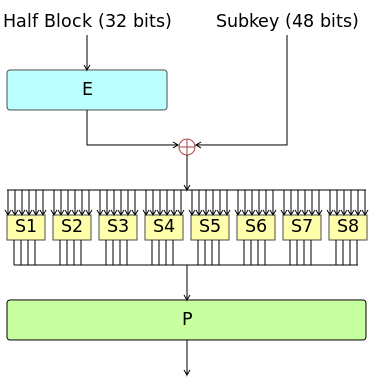
0-9
.NET
|
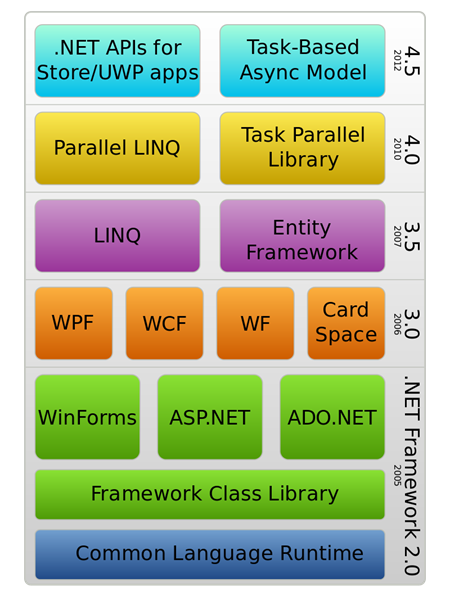
.NET Framework (pronounced dot net) is a software framework developed by
Microsoft that runs primarily on Microsoft Windows. It includes a large class library
named Framework Class Library (FCL) and provides language
interoperability (each language can use code written in other languages)
across several programming languages. Programs written for .NET
Framework execute in a software environment (in contrast to a hardware
environment) named Common Language Runtime (CLR), an application virtual
machine that provides services such as security, memory management, and
exception handling. (As such, computer code written using .NET Framework is
called "managed code".) FCL and CLR together constitute .NET
Framework. |
|
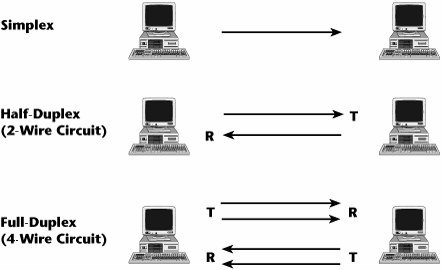
100 Mbps—Fast Ethernet
|
In computer networking, Fast Ethernet physical layers carry traffic at the
nominal rate of 100 Mbit/s. The prior Ethernet speed was 10 Mbit/s. Of the
Fast Ethernet physical layers, 100BASE-TX is by far the most common. |
|
5ESS
|
5ESS Switching System |
The 5ESS Switching System is a telephone electronic switching system
developed by Western Electric for the American Telephone and Telegraph
Company (AT&T) and the Bell System in the United States. |
5G
|
5G is a marketing term for some new mobile technologies. Definitions
differ and confusion is common. The ITU IMT-2020 standard provides for speeds
up to 20 gigabits per second and has only been demonstrated with millimeter waves of 15 gigahertz and higher frequency.
The more recent 3GPP standard includes any network using the NR New Radio
software. 5G New Radio can include lower frequencies, from 600 MHz to 6 GHz.
However, the speeds in these lower frequencies are only modestly higher than
new 4G systems, estimated at 15% to 50% faster. At least at the lower
frequencies, "5G is evolutionary." |
|
802.3 Physical Layer
|
EEE 802.3 is a working group and a collection of Institute of Electrical
and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) standards produced by the working group
defining the physical layer and data link layer's media access control (MAC)
of wired Ethernet. This is generally a local area network (LAN) technology
with some wide area network (WAN) applications. Physical connections are made
between nodes and/or infrastructure devices (hubs, switches, routers) by
various types of copper or fiber cable. |
|
802.11
|
EEE 802.11 is part of the IEEE 802 set of local area network (LAN)
technical standards, and specifies the set of media
access control (MAC) and physical layer (PHY) protocols for implementing
wireless local area network (WLAN) computer communication. The standard and
amendments provide the basis for wireless network products using the Wi-Fi
brand and are the world's most widely used wireless computer networking
standards. IEEE 802.11 is used in most home and office networks to allow
laptops, printers, smartphones, and other devices to communicate with each
other and access the Internet without connecting wires. The standards are created and maintained by the Institute of Electrical
and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) LAN/MAN Standards Committee (IEEE 802). The
base version of the standard was released in 1997 and has had subsequent
amendments. While each amendment is officially revoked when it is
incorporated in the latest version of the standard, the corporate world tends
to market to the revisions because they concisely denote the capabilities of
their products. As a result, in the marketplace, each revision tends to
become its own standard. IEEE 802.11 uses various frequencies including, but not limited to, 2.4
GHz, 5 GHz, 6 GHz, and 60 GHz frequency bands. Although IEEE 802.11
specifications list channels that might be used, the radio frequency spectrum
availability allowed varies significantly by regulatory domain. The protocols are typically used in conjunction with IEEE 802.2, and are
designed to interwork seamlessly with Ethernet, and are very often used to
carry Internet Protocol traffic. |
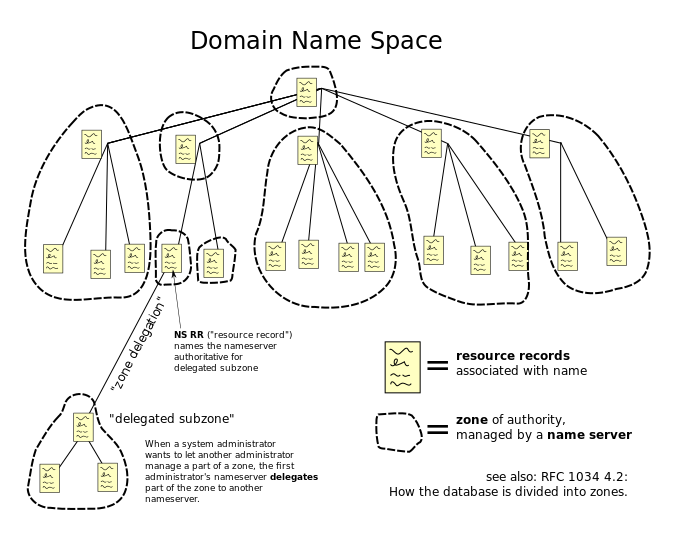
A
|
Authoritative Answer |
Specifies that the responding name server is an authority for the domain name in question section. Note that the contents of the answer section may have multiple owner names because of aliases. This bit corresponds to the name which matches the query name, or the first owner name in the answer section. |
|
|
Advanced Audio Coding |
Advanced Audio Coding (AAC) is a proprietary audio coding standard for
lossy digital audio compression. Designed to be the successor of the MP3
format, AAC generally achieves better sound quality than MP3 at the same bit
rate. The confusingly named AAC+ (HE-AAC) does so only at low bit rates and
less so at high ones. |
|
|
An ATM Adaptation layer 1 or AAL1 is used for transmitting Class A network traffic, that is, real-time, constant bit rate, connection oriented traffic (example- uncompressed audio and video). Bits are fed in by the application at constant rate and must be delivered to other end with minimum delay, jitter or overhead. The input is stream of bits without message boundaries. For this traffic, error detection protocols cannot be used since timeouts and retransmission causes delay but the missing cells are reported to the application, that must take its own action to recover from them. |
||
|
ATM Adaptation Layer 2 |
ATM Adaptation Layer 2 (AAL2) is an ATM adaptation layer for Asynchronous
Transfer Mode (ATM), used primarily in telecommunications; for example, it is
used for the Iu interfaces in the Universal Mobile
Telecommunications System, and is also used for transporting digital voice.
The standard specifications related to AAL2 are ITU standards I.363.2 and
I366.1. |
|
|
ATM Adaptation Layer 5 |
ATM Adaptation Layer 5 (AAL5) is an ATM adaptation layer used to send
variable-length packets up to 65,535 octets in size across an Asynchronous
Transfer Mode (ATM) network. |
|
Acceptance
Test
|
Formal test defining acceptance criteria for a release. |
|
|
An acceptance test is a formal description of the behavior of a software product, generally expressed as an example or a usage scenario. A number of different notations and approaches have been proposed for such examples or scenarios. In many cases the aim is that it should be possible to automate the execution of such tests by a software tool, either ad-hoc to the development team or off the shelf. |
||
Activity
|
An element of work performed during a project, normally associated with an expected resource usage. The terms activities and tasks are somewhat interchangeable, although the PMBOK defines tasks as resulting from the breakdown of activities. |
|
Activity
Model
|
Specifies work or workflow by showing and describing the states and flow of control of the system or process. |
|
|
Active Directory |
Active Directory (AD) is a directory service that Microsoft developed for
the Windows domain networks. It is included in most Windows Server operating
systems as a set of processes and services. Initially, Active Directory was
only in charge of centralized domain management. Starting with Windows Server
2008, however, Active Directory became an umbrella title for a broad range of
directory-based identity-related services. |
|
Ad
Hoc Testing
|
See informal testing. |
|
Ada
|
Ada is a structured, statically typed, imperative, and object-oriented high-level computer programming language, extended from Pascal and other languages. It has built-in language support for design-by-contract, extremely strong typing, explicit concurrency, tasks, synchronous message passing, protected objects, and non-determinism. Ada improves code safety and maintainability by using the compiler to find errors in favor of runtime errors. Ada is an international standard; the current version (known as Ada 2012) is defined by ISO/IEC 8652:2012. |
|
|
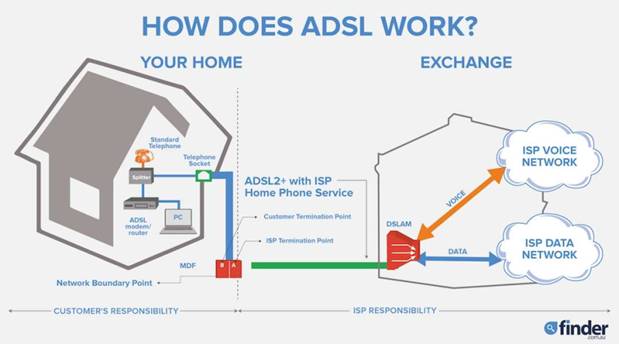
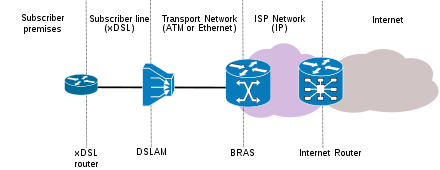
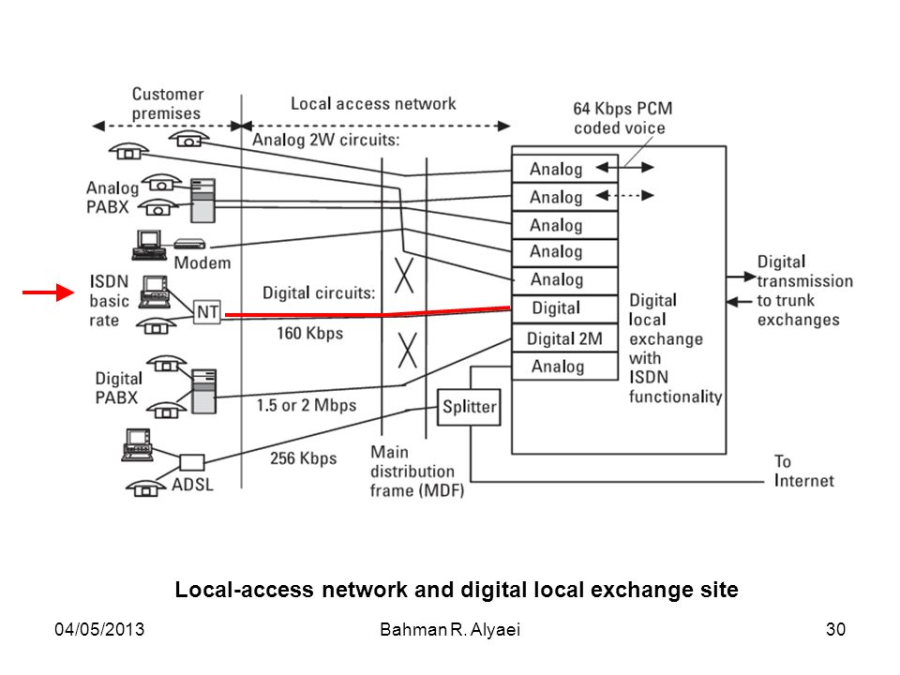
Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Loop |
Asymmetric digital subscriber line (ADSL) is a type of digital subscriber
line (DSL) technology, a data communications technology that enables faster
data transmission over copper telephone lines than a conventional voiceband
modem can provide. ADSL differs from the less common symmetric digital
subscriber line (SDSL). In ADSL, bandwidth and bit rate are said to be
asymmetric, meaning greater toward the customer premises (downstream) than
the reverse (upstream). Providers usually market ADSL as a service for
consumers for Internet access for primarily downloading content from the
Internet, but not serving content accessed by others.
|
|
AES
|
Advanced Encryption Standard |
The Advanced Encryption Standard (AES), also known by its original name
Rijndael is a specification for the encryption of electronic data established
by the U.S. National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) in 2001. |
Agent
|
In a project charter, responsible for initiating, sponsoring, and supporting the project. Also see project sponsor. |
|
|
a project management approach based on delivering requirements iteratively and incrementally throughout the life cycle. |
||
|
an umbrella term specifically for iterative software development methodologies. Popular methods include Scrum, Lean, DSDM and eXtreme Programming (XP). |
||
|
Describes the four principles of agile development:
|
||
|
Alarm Indication Signaling |
Alarm indication signal (AIS) (also called "all ones" because of the data and framing pattern) is a signal transmitted by an intermediate element of a multi-node transport circuit that is part of a concatenated telecommunications system to alert the receiving end of the circuit that a segment of the end-to-end link has failed at a logical or physical level, even if the system it is directly connected to is still working. The AIS replaces the failed data, allowing the higher order system in the concatenation to maintain its transmission framing integrity. Downstream intermediate elements of the transport circuit propagate the AIS onwards to the destination element. |
|
|
An A-law algorithm is a standard companding algorithm, used in European 8-bit PCM digital communications systems to optimize, i.e. modify, the dynamic range of an analog signal for digitizing. It is one of two versions of the G.711 standard from ITU-T, the other version being the similar µ-law, used in North America and Japan. |
||
|
Access Link Control Application Protocol |
Control plane protocol for the transport
layer in 3rd Generation UMTS networks is called ALCAP ("Access Link
Control Application Part"). ALCAP is defined by 3GPP as equivalent of
ITU recommendation Q.2630.2. Basic functionality of ALCAP is multiplexing of
different users onto one AAL2 transmission path using channel IDs (CIDs). It
is used in the UMTS access network UTRAN along with ATM, while IPBCP is use
for IP links in the core of the network. |
|
|
Amazon Electric Compute Cloud |
Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2) forms a central part of Amazon.com's cloud-computing platform, Amazon Web Services (AWS), by allowing users to rent virtual computers on which to run their own computer applications. EC2 encourages scalable deployment of applications by providing a web service through which a user can boot an Amazon Machine Image (AMI) to configure a virtual machine, which Amazon calls an "instance", containing any software desired. A user can create, launch, and terminate server-instances as needed, paying by the second for active servers – hence the term "elastic". EC2 provides users with control over the geographical location of instances that allows for latency optimization and high levels of redundancy. |
|
|
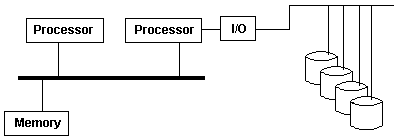
Asymmetric Multiprocessing |
In an asymmetric multiprocessing system (AMP), not all CPUs are treated
equally; for example, a system might allow (either at the hardware or
operating system level) only one CPU to execute operating system code or
might allow only one CPU to perform I/O operations. Other AMP systems would
allow any CPU to execute operating system code and perform I/O operations, so
that they were symmetric with regard to processor
roles, but attached some or all peripherals to particular CPUs, so that they
were asymmetric with respect to the peripheral attachment. Asymmetric
multiprocessing was the only method for handling multiple CPUs before
symmetric multiprocessing (SMP) was available. It has also been used to
provide less expensive options on systems where SMP was available.
Additionally, AMP is used in applications that are dedicated, such as
embedded systems, when individual processors can be dedicated to specific
tasks at design time. |
|
|
Adaptive Multi-Rate Narrow band |
The Adaptive Multi-Rate (AMR, AMR-NB or GSM-AMR) audio codec is an audio
compression format optimized for speech coding. AMR speech codec consists of
a multi-rate narrowband speech codec that encodes narrowband (200–3400 Hz)
signals at variable bit rates ranging from 4.75 to 12.2 kbit/s with toll
quality speech starting at 7.4 kbit/s. |
|
|
Adaptive Multi-Rate Wideband |
Adaptive Multi-Rate Wideband (AMR-WB) is a patented wideband speech audio
coding standard developed based on Adaptive Multi-Rate encoding, using
similar methodology as algebraic code excited linear prediction (ACELP).
AMR-WB provides improved speech quality due to a wider speech bandwidth of
50–7000 Hz compared to narrowband speech coders which in general are
optimized for POTS wireline quality of 300–3400 Hz. AMR-WB was developed by
Nokia and VoiceAge and it was first specified by
3GPP.
|
|
Analogy
Estimation
|
Creating estimates by using expert judgment to compare proposed work to historical data for similar past work. Often coupled with fuzzy logic techniques. |
|
|
Android is a mobile operating system developed by Google, based on a modified version of the Linux kernel and other open source software and designed primarily for touchscreen mobile devices such as smartphones and tablets. In addition, Google has further developed Android TV for televisions, Android Auto for cars, and Wear OS for wrist watches, each with a specialized user interface. Variants of Android are also used on game consoles, digital cameras, PCs and other electronics. |
||
|
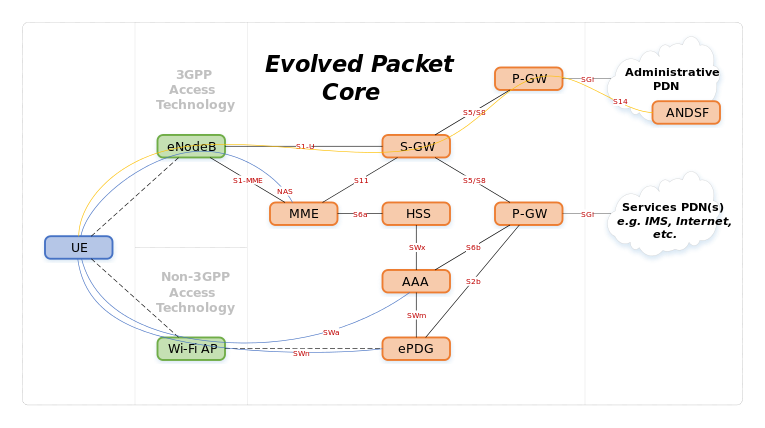
Access Network Discovery and Selection Function |
The ANDSF provides information to the UE about connectivity to 3GPP and
non-3GPP access networks (such as Wi-Fi). The purpose of the ANDSF is to
assist the UE to discover the access networks in their vicinity and to
provide rules (policies) to prioritize and manage connections to these
networks. |
|
|
American National Standards Institute |
The American National Standards Institute is a private non-profit
organization that oversees the development of voluntary consensus standards
for products, services, processes, systems, and personnel in the United
States. The organization also coordinates U.S. standards with international
standards so that American products can be used worldwide. |
|
|
are common solutions to common problems where the solution is ineffective and may result in undesired consequences. |
||
|
Anycast is a network addressing and routing methodology in which a single
destination address has multiple routing paths to two or more endpoint
destinations. Routers will select the desired path on the
basis of number of hops, distance, lowest cost, latency measurements
or based on the least congested route. Anycast networks are widely used for
CDN products to bring their content closer to the end user. |
||
|
aspect-oriented programming |
In computing, aspect-oriented programming (AOP) is a programming paradigm
that aims to increase modularity by allowing the separation of cross-cutting
concerns. It does so by adding additional behavior
to existing code (an advice) without modifying the
code itself, instead separately specifying which code is modified via a
"pointcut" specification, such as "log all function calls when
the function's name begins with 'set'". This allows behaviors
that are not central to the business logic (such as logging) to be added to a
program without cluttering the code, core to the functionality. AOP forms a
basis for aspect-oriented software development. |
|
|
application programming interface |
a specific method prescribed by a computer operating system or by an application program by which a programmer writing an application program can make requests of the operating system or another application. |
|
|
Access Point Name |
An Access Point Name (APN) is the name of a gateway between a GSM, GPRS,
3G or 4G mobile network and another computer network, frequently the public
Internet. |
|
Architecture
|
Top level overview and plan for a software system. See CxStand_Design for more information. |
|
|
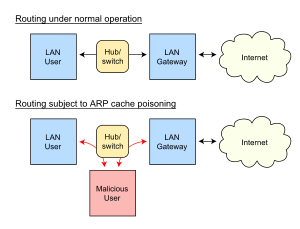
In computer networking, ARP spoofing, ARP cache poisoning, or ARP poison
routing, is a technique by which an attacker sends (spoofed) Address
Resolution Protocol (ARP) messages onto a local area network. Generally, the
aim is to associate the attacker's MAC address with the IP address of another
host, such as the default gateway, causing any traffic meant for that IP
address to be sent to the attacker instead. |
||
Artifact
|
The tangible result of work performed. |
|
|
ASCII, abbreviated from American Standard Code for Information
Interchange, is a character encoding standard for electronic communication.
ASCII codes represent text in computers, telecommunications equipment, and
other devices. Most modern character-encoding schemes are based on ASCII,
although they support many additional characters. |
||
|
Abstract Syntax Notation One (ASN.1) is an interface description language for defining data structures that can be
serialized and deserialized in a standard, cross-platform way. It is broadly
used in telecommunications and computer networking, and especially in
cryptography. |
||
Assessment
|
A review of the state or practices of a project or organization, often performed by an independent entity. |
|
|
Acceptance Test Driven Development |
involves team members with different perspectives (customer, development, testing) collaborating to write acceptance tests in advance of implementing the corresponding functionality. |
|
|
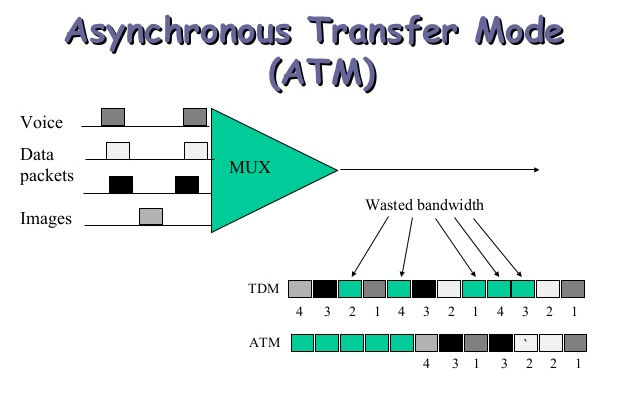
Asynchronous Transfer Mode |
Asynchronous transfer mode (ATM) is, according to the ATM Forum, "a
telecommunications concept defined by ANSI and ITU (formerly CCITT) standards
for carriage of a complete range of user traffic, including voice, data, and
video signals".[1] ATM was developed to meet the needs of the Broadband
Integrated Services Digital Network, as defined in the late 1980s,[2] and
designed to integrate telecommunication networks. Additionally, It was designed for networks that must handle both
traditional high-throughput data traffic (e.g., file transfers), and
real-time, low-latency content such as voice and video. The reference model
for ATM approximately maps to the three lowest layers of the ISO-OSI
reference model: network layer, data link layer, and physical layer.[3] ATM
is a core protocol used over the SONET/SDH backbone of the public switched
telephone network (PSTN) and Integrated Services Digital Network (ISDN), but
its use is declining in favour of all IP. |
|
|
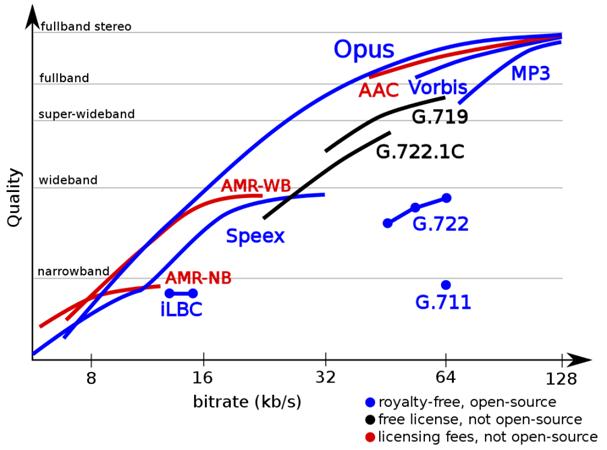
An audio coding format (or sometimes audio compression format) is a
content representation format for storage or transmission of digital audio
(such as in digital television, digital radio and in audio and video files).
Examples of audio coding formats include MP3, AAC, Vorbis,
FLAC, and Opus. A specific software or hardware implementation capable of
audio compression and decompression to/from a specific audio coding format is
called an audio codec; an example of an audio codec is LAME, which is one of
several different codecs which implements encoding and decoding audio in the
MP3 audio coding format in software. |
||
Audit
|
Sometimes used as a synonym for assessment, usually in a more formal and independent context. |
|
Author
|
For a review, the person assigned to represent the author viewpoint for an artifact. The author is normally the primary contributor to the creation of the artifact. |
|
Authority
|
Responsible for funding and championing a project, the project sponsor. |
|
|
In the context of software development, build refers to the process that converts files and other assets under the developers' responsibility into a software product in its final or consumable form. The build is automated when these steps are repeatable, require no direct human intervention, and can be performed at any time with no information other than what is stored in the source code control repository. |
||
Automated
Testing
|
The use of tools and technology to encode, execute, and note results of test cases on a system without human intervention. |
|
|
AWK is a programming language designed for
text processing and typically used as a data extraction and reporting tool.
It is a standard feature of most Unix-like operating systems. |
||
|
Amazon Web Services |
Amazon Web Services (AWS) is a subsidiary of Amazon.com that provides on-demand cloud computing platforms to individuals, companies and governments, on a paid subscription basis. The technology allows subscribers to have at their disposal a virtual cluster of
computers, available all the time, through the Internet. AWS's version of
virtual computers emulate most of the attributes of a real computer including
hardware (CPU(s) & GPU(s) for processing, local/RAM memory, hard-disk/SSD storage); a choice of operating systems;
networking; and pre-loaded application software such as web servers,
databases, CRM, etc. Each AWS system also virtualizes its console I/O
(keyboard, display, and mouse), allowing AWS subscribers to connect to their
AWS system using a modern browser. The browser acts as a window into the
virtual computer, letting subscribers log-in, configure and use their virtual
systems just as they would a real physical computer. They can choose to
deploy their AWS systems to provide internet-based services for themselves
and their customers. |
|
|
Microsoft Azure is a cloud computing service created by Microsoft for building, testing, deploying, and managing applications and services through a global network of Microsoft-managed data centers. It provides software as a service (SaaS), platform as a service (PaaS) and infrastructure as a service (IaaS) and supports many different programming languages, tools and frameworks, including both Microsoft-specific and third-party software and systems. |