B2B | business-to-business | Business-to-business (B2B or, in some countries, BtoB) refers to a situation where one business makes a commercial transaction with another. This typically occurs when: |
B2C | business-to-consumer | Business to consumer (B2C) refers to the transactions conducted directly between a company and consumers who are the end-users of its products or services. The business to consumer as a business model differs significantly from the business-to-business model, which refers to commerce between two or more businesses. While most companies that sell directly to consumers can be referred to as B2C companies, the term became immensely popular during the dotcom boom of the late 1990s, when it was used mainly to refer to online retailers, as well as other companies that sold products and services to consumers through the internet. |
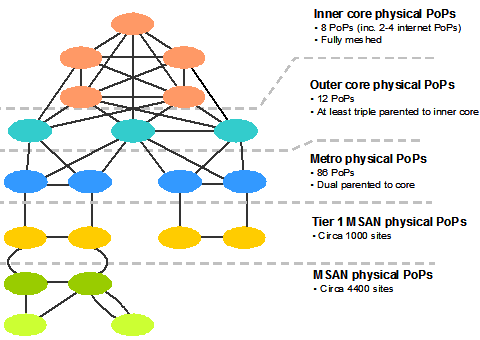
Backhaul | In a hierarchical telecommunications network the backhaul portion of the network comprises the intermediate links between the core network, or backbone network, and the small subnetworks at the "edge" of the entire hierarchical network. | |
Backlog | A backlog is an ordered list of items representing everything that may be needed to deliver a specific outcome. There are different types of backlogs depending on the type of item they contain and the approach being used. | |
Backlog Grooming | Backlog grooming is when the product owner and some, or all, of the rest of the team refine the backlog on a regular basis to ensure the backlog contains the appropriate items, that they are prioritized, and that the items at the top of the backlog are ready for delivery. | |
Bandwidth | Bandwidth is the maximum rate of data transfer across a given path. Bandwidth may be characterized as network bandwidth, data bandwidth, or digital bandwidth. | |
Baseline | The original version of an artifact that serves as the basis for all future development work. Baselined artifacts are normally placed under change control. | |
Bash | Bash is a Unix shell and command language written by Brian Fox for the GNU Project as a free software replacement for the Bourne shell. First released in 1989, it has been distributed widely as the default login shell for most Linux distributions and Apple's macOS (formerly OS X). A version is also available for Windows 10. It is also the default user shell in Solaris 11. | |
BASIC | BASIC (an acronym for Beginner's All-purpose Symbolic Instruction Code) is a family of general-purpose, high-level programming languages whose design philosophy emphasizes ease of use. In 1964, John G. Kemeny, Thomas E. Kurtz and Sr. Mary Kenneth Keller designed the original BASIC language at Dartmouth College. They wanted to enable students in fields other than science and mathematics to use computers. At the time, nearly all use of computers required writing custom software, which was something only scientists and mathematicians tended to learn. | |
BAU | Business as Usual | Business as usual (BAU) - the normal execution of standard functional operations within an organization - forms a possible contrast to projects or programmes which might introduce change.[citation needed] BAU may also stand in contradistinction to external events which may have the effect of unsettling or distracting those inside an organisation |
BDD | Behavior Driven Development (BDD) | BDD is a practice where members of the team discuss the expected behavior of a system in order to build a shared understanding of expected functionality. |
Bench Test | A test that is performed in the development environment and focuses on the part of the system being worked on. | |
BER | Bit Error Rate | In digital transmission, the number of bit errors is the number of received bits of a data stream over a communication channel that have been altered due to noise, interference, distortion or bit synchronization errors. |
BER | Basic Encoding Rules | The format for Basic Encoding Rules specifies a self-describing and self-delimiting format for encoding ASN.1 data structures. Each data element is encoded as a type identifier, a length description, the actual data elements, and, where necessary, an end-of-content marker. These types of encodings are commonly called type-length-value or TLV encodings. This format allows a receiver to decode the ASN.1 information from an incomplete stream, without requiring any pre-knowledge of the size, content, or semantic meaning of the data. |
Best Practice | A practice, technique, process, or idiom that has been proven effective and/or efficient for completing a goal or addressing common risks. See CxOne Best Practice material type. | |
Best Practice Description | CxBest | CxOne best practice material type, see CxOneOverview for description. |
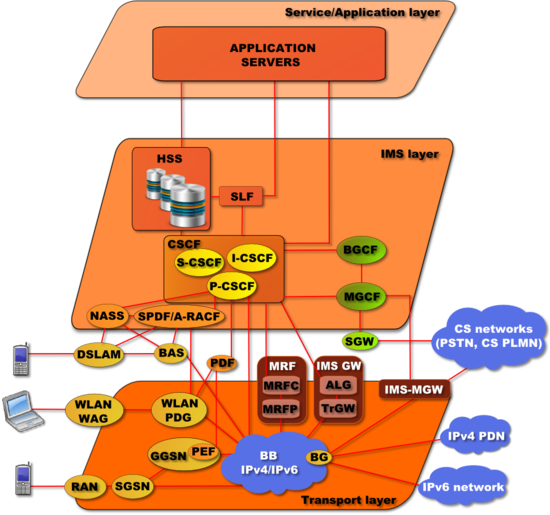
BGCF | Breakout Gateway Control Function | A Breakout Gateway Control Function (BGCF) is a SIP proxy which processes requests for routing from an S-CSCF when the S-CSCF has determined that the session cannot be routed using DNS or ENUM/DNS. It includes routing functionality based on telephone numbers. |
BGP | Border Gateway Protocol | Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) is a standardized exterior gateway protocol designed to exchange routing and reachability information among autonomous systems (AS) on the Internet. The protocol is classified as a path vector protocol. The Border Gateway Protocol makes routing decisions based on paths, network policies, or rule-sets configured by a network administrator and is involved in making core routing decisions. |
Bjarne Stroustrup | Bjarne Stroustrup is a Danish computer scientist, who is most notable for the creation and development of the widely used C++ programming language. | |
Black-Box Testing | Synonym for functional testing. | |
Bluetooth | Bluetooth is a wireless technology standard for exchanging data over short distances (using short-wavelength UHF radio waves in the ISM band from 2.4 to 2.485 GHz) from fixed and mobile devices, and building personal area networks (PANs). Invented by Dutch electrical engineer Jaap Haartsen, working for telecom vendor Ericsson in 1994, it was originally conceived as a wireless alternative to RS-232 data cables. | |
BNF | Backus–Naur form | In computer science, Backus–Naur form or Backus normal form (BNF) is a metasyntax notation for context-free grammars, often used to describe the syntax of languages used in computing, such as computer programming languages, document formats, instruction sets and communication protocols. They are applied wherever exact descriptions of languages are needed: for instance, in official language specifications, in manuals, and in textbooks on programming language theory. Many extensions and variants of the original Backus–Naur notation are used; some are exactly defined, including extended Backus–Naur form (EBNF) and augmented Backus–Naur form (ABNF). <postal-address> ::= <name-part> <street-address> <zip-part>
<name-part> ::= <personal-part> <last-name> <opt-suffix-part> <EOL> | <personal-part> <name-part>
<personal-part> ::= <initial> "." | <first-name>
<street-address> ::= <house-num> <street-name> <opt-apt-num> <EOL>
<zip-part> ::= <town-name> "," <state-code> <ZIP-code> <EOL>
<opt-suffix-part> ::= "Sr." | "Jr." | <roman-numeral> | ""
<opt-apt-num> ::= <apt-num> | ""
|
BNG | Broadband Network Gateway | The Broadband Network Gateway (BNG) allows subscribers to connect to a broadband network through an access portal. It creates and manages subscriber sessions, aggregating traffic from various subscriber sessions from an access network, and routing it to the network of the Internet Service Provider (ISP) or Network Service Provider (NSP). |
BOOTP | Dynamic IP Address Allocation – Bootstrap protocol | The Bootstrap Protocol (BOOTP) is a computer networking protocol used in Internet Protocol networks to automatically assign an IP address to network devices from a configuration server. The BOOTP was originally defined in RFC 951. |
Boston Matrix | The growth–share matrix (aka the product portfolio matrix,[ Boston Box, BCG-matrix, Boston matrix, Boston Consulting Group analysis, portfolio diagram) is a chart that to help corporations to analyze their business units, that is, their product lines. This helps the company allocate resources and is used as an analytical tool in brand marketing, product management, strategic management, and portfolio analysis. Some analysis of market performance by firms using its principles has called its usefulness into question. | |
Bottom-Up Estimation | Estimating a system by decomposing it and then estimating each decomposed piece individually, rolling up the total to get an entire system estimate. | |
BPEL | Business Process Execution Language | BPEL (Business Process Execution Language) is an XML-based language that allows Web services in a service-oriented architecture (SOA) to interconnect and share data. |
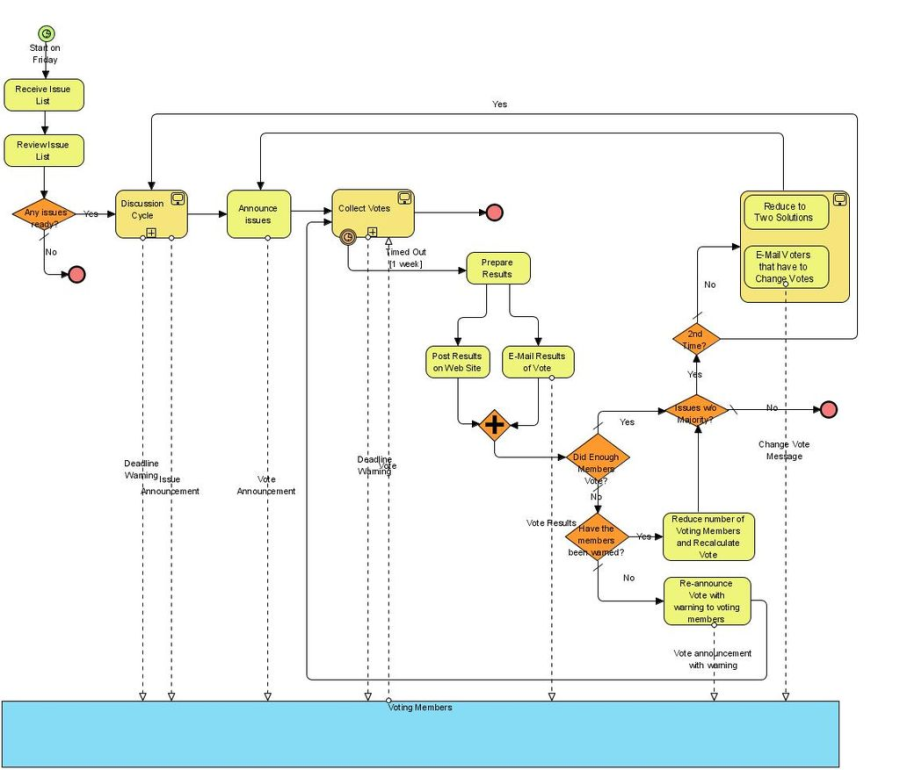
BPMN | Business Process Model and Notation | Business Process Model and Notation (BPMN) is a graphical representation for specifying business processes in a business process model. |
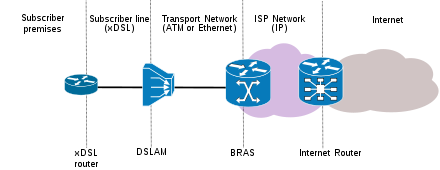
BRAS | Broadband Remote Access Server | A broadband remote access server (BRAS, B-RAS or BBRAS) routes traffic to and from broadband remote access devices such as digital subscriber line access multiplexers (DSLAM) on an Internet service provider's (ISP) network |
Broadcast | In computer networking, telecommunication and information theory, broadcasting is a method of transferring a message to all recipients simultaneously. Broadcasting can be performed as a high level operation in a program, for example broadcasting Message Passing Interface, or it may be a low level networking operation, for example broadcasting on Ethernet. | |
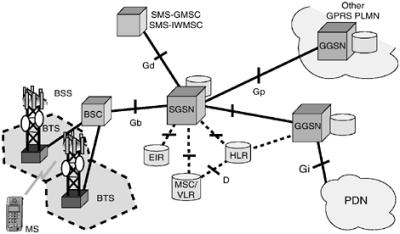
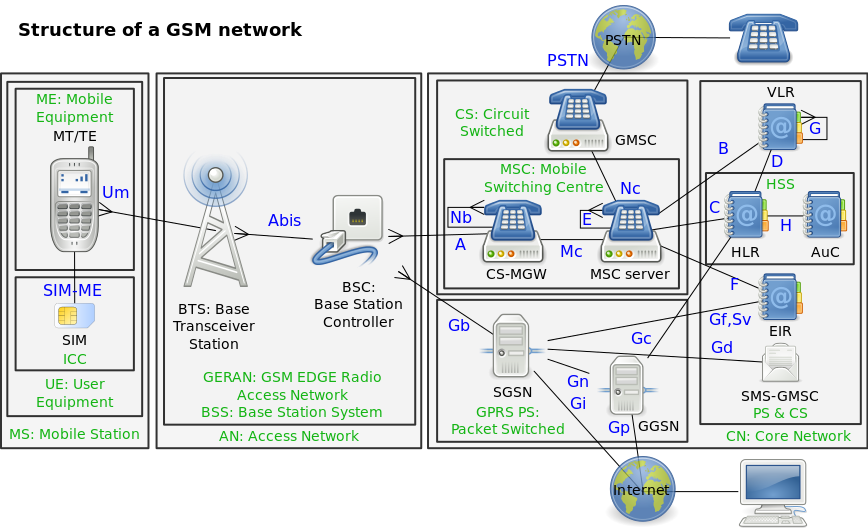
BSC | The base station controller (BSC) provides, classically, the intelligence behind the BTSs. Typically a BSC has tens or even hundreds of BTSs under its control. The BSC handles allocation of radio channels, receives measurements from the mobile phones, and controls handovers from BTS to BTS (except in the case of an inter-BSC handover in which case control is in part the responsibility of the anchor MSC). A key function of the BSC is to act as a concentrator where many different low capacity connections to BTSs (with relatively low utilisation) become reduced to a smaller number of connections towards the mobile switching center (MSC) (with a high level of utilisation). Overall, this means that networks are often structured to have many BSCs distributed into regions near their BTSs which are then connected to large centralised MSC sites. | |
BSS | Base station subsystem | The base station subsystem (BSS) is the section of a traditional cellular telephone network which is responsible for handling traffic and signaling between a mobile phone and the network switching subsystem. The BSS carries out transcoding of speech channels, allocation of radio channels to mobile phones, paging, transmission and reception over the air interface and many other tasks related to the radio network.
|
BSS | Business support systems | Business support systems (BSS) are the components that a telecommunications service provider (or telco) uses to run its business operations towards customers. |
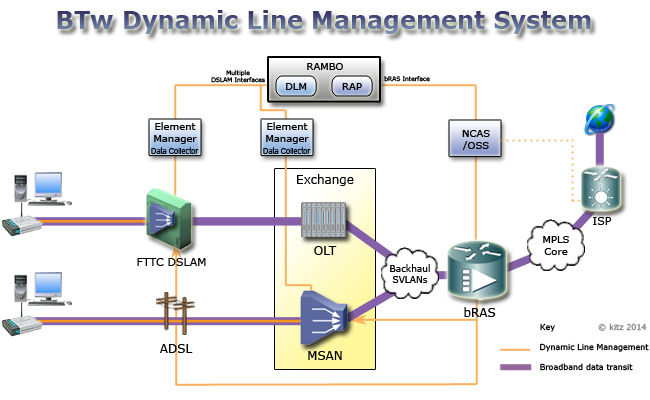
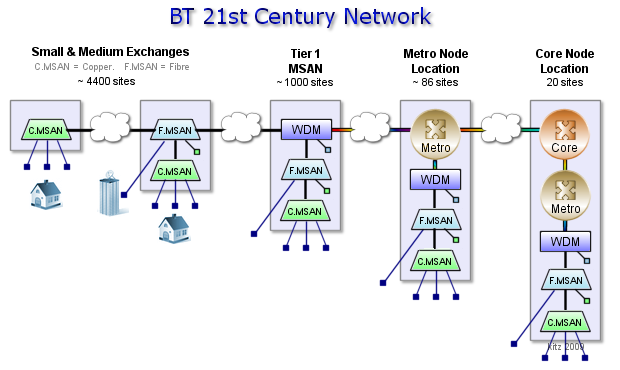
BT 21CN | BT 21st Century Network | 21CN involves a huge overhaul of the existing 20CN network. Over the next few years BT will gradually be updating the existing equipment and replacing it with a new multi-service network. |
BTNUP | See IUP | |
BTS | Base Transceiver Station | A base transceiver station (BTS) is a piece of equipment that facilitates wireless communication between user equipment (UE) and a network. UEs are devices like mobile phones (handsets), WLL phones, computers with wireless Internet connectivity. The network can be that of any of the wireless communication technologies like GSM, CDMA, wireless local loop, Wi-Fi, WiMAX or other wide area network (WAN) technology. |
bug | a coding error in a computer program. | |
Build | The process of executing a software build, which is normally largely automated. Also refers to the resulting output, which is a built version of a system, ready for testing. | |
Build Environment | A development environment that is isolated and dedicated to the create of builds. Normally one or more dedicate build machines. | |
Build Machine | A computer dedicated to the create of software builds. | |
build tool | a programming utility that is used when building a new version of a program. | |
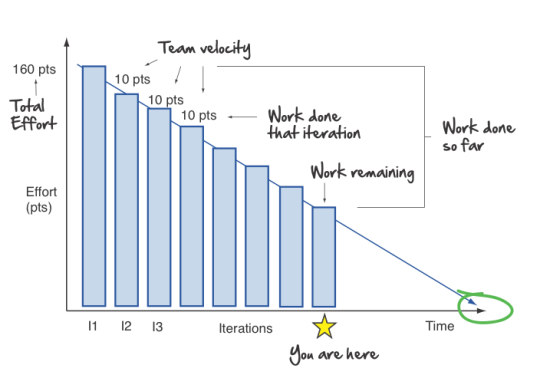
Burndown Chart | Burndown charts and burnup charts track the amount of output (in terms of hours, story points, or backlog items) a team has completed across an iteration or a project. | |
Burst | In telecommunication, a burst transmission or data burst is the broadcast of a relatively high-bandwidth transmission over a short period. | |
Business Agility Ownership | Business agility is the ability of an organization to sense changes internally or externally and respond accordingly in order to deliver value to its customers. | |
Business Requirement | High level objectives of the organization or customer requesting a system or product. Also known as the Why Requirements. | |
Business Schedule | High level project schedule containing top level milestones and their associated business goals for the entire project. A business schedule often defines a set of top-down schedule constraints that will be managed to. Compare to detailed schedule. | |
BYOD | Bring your own device | Bring your own device (BYOD)—also called bring your own technology (BYOT), bring your own phone (BYOP), and bring your own personal computer (BYOPC)—refers to the policy of permitting employees to bring personally owned devices (laptops, tablets, and smart phones) to their workplace, and to use those devices to access privileged company information and applications. The phenomenon is commonly referred to as IT consumerization. |